
Ten opis pochodzi ze strony producenta / dystrybutora.
Doppelherz aktiv Aktiv-Meno – suplement diety przeznaczony dla kobiet z objawami menopauzy i po okresie menopauzy.
- Izoflawony sojowe są fitoestrogenami, budową zbliżoną do żeńskich hormonów płciowych, dzięki czemu wspomagają łagodzenie dolegliwości związanych z menopauzą. Mają zdolność wiązania się z receptorami estrogenowymi i przekazywania odpowiedniego sygnału hormonalnego.
- Witaminy B6, B7 i B12 wspierają procesy koncentracji i przyczyniają się do lepszego zapamiętywania.
- Witaminy B2 i B9 wspomagają funkcje emocjonalne i pomagają zminimalizować skutki zmęczenia i znużenia.
- Wapń i witamina D3 wpływają korzystnie na prawidłową mineralizacje w tkance kostnej oraz na jej odbudowe i wzmocnienie. Jest to szczególnie istotne dla kobiet w okresie menopauzalnym i po menopauzie.
Doppelherz aktiv Aktiv-Meno – Składniki
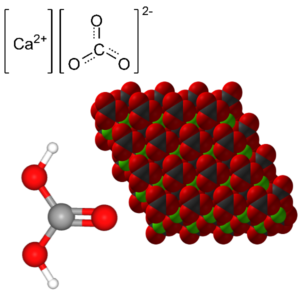
- Wapń
- Wapń (Węglan Wapnia) (CaCO3 or CCaO3)
 Wapń (Węglan Wapnia): Calcium Carbonate, Limestone, Marble, Chalk, Calcite,
Wapń (Węglan Wapnia): Calcium Carbonate, Limestone, Marble, Chalk, Calcite,
PubChem CID: 10112,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 471-34-1,
ChemIDplus: 471-34-1,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A02AC01,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: H0G9379FGK,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS4E2000-3.
- Wapń (Węglan Wapnia) (CaCO3 or CCaO3)
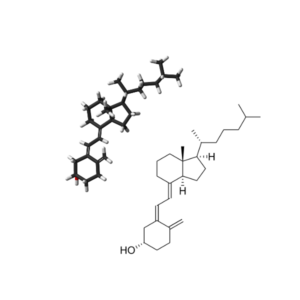
- Witamina D
- Witamina D3 (Cholekalcyferol) (C27H44O)
 Witamina D3 (Cholekalcyferol): Cholecalciferol, Vitamin D3, Calciol, Colecalciferol,
Witamina D3 (Cholekalcyferol): Cholecalciferol, Vitamin D3, Calciol, Colecalciferol,
PubChem CID: 5280795,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 67-97-0,
ChemIDplus: 67-97-0,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11CC05,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 1C6V77QF41,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2C1910,
References:
Weight Loss: CEFALO, Chiara MA; CONTE, C.; SORICE, G. P.; MOFFA, S.; SUN, V. A.; CINTI, F.; SALOMONE, E.; MUSCOGIURI, G.; BROCCHI, A. A. G.; PONTECORVI, A.; MEZZA, T.; GIACCARI, A. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Obesity‐Induced Insulin Resistance: A Double‐Blind, Randomized, Placebo‐Controlled Trial. Obesity, 2018, 26.4: 651-657. PMID:29504254.
- Witamina D3 (Cholekalcyferol) (C27H44O)
- Witamina B
- Witamina B1 (Tiamina/Aneurina) (C12H17N4OS+)
Osiem witamin z grupy B pomaga organizmowi przekształcać żywność, zwłaszcza węglowodany, w glukozę, którą może wykorzystać jako energię. Witamina B1 nie jest inna – pomaga również metabolizować tłuszcze i białka, zapewniając, że otrzymujesz wszystkie potrzebne składniki odżywcze z pożywienia. Witamina B1 (Tiamina/Aneurina): Thiamine, Vitamin B1, Aneurin, Antiberiberi Factor, Thiadoxine, Betaxin, Thiamin,
Witamina B1 (Tiamina/Aneurina): Thiamine, Vitamin B1, Aneurin, Antiberiberi Factor, Thiadoxine, Betaxin, Thiamin,
PubChem CID: 1130,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 70-16-6,
ChemIDplus: 70-16-6,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11DA01,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: X66NSO3N35,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2A6B60,
References:
Weight Loss: KERNS, Jennifer C.; ARUNDEL, Cherinne; CHAWLA, Lakhmir S. Thiamin deficiency in people with obesity. Advances in nutrition, 2015, 6.2: 147-153. PMID:25770253,
Brain / Mental Clarity: BOURRE, Jean-Marie Effects of nutrients (in food) on the structure and function of the nervous system: update on dietary requirements for brain. Part 1: micronutrients. Journal of Nutrition Health and Aging, 2006, 10.5: 377. PMID:17066209, KENNEDY, David O. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy–A Review. Nutrients, 2016, 8.2: 68. PMID:26828517.
- Witamina B1 (Azotan Tiaminy) (C12H17N5O4S)
Witamina B1 (Azotan Tiaminy): Thiamine Nitrate, Thiamine Mononitrate, Vitamin B1 Nitrate, Vitamin B1 Mononitrate, Aneurine Mononitrate, Aneurine Nitrate, Betabion Mononitrate, Thiamine Nitrate (Salt), Thiamine Nitronate, PubChem CID: 10762, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 532-43-4, ChemIDplus: 532-43-4, WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11DA01, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 8K0I04919X, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2A6B60-1.
- Witamina B2 (Ryboflawina) (C17H20N4O6)
 Witamina B2 (Ryboflawina): Riboflavin, Riboflavina, Riboflavinum, Vitamin B2, Lactoflavin, Riboflavine, Vitamin G, Beflavin, Beflavine,
Witamina B2 (Ryboflawina): Riboflavin, Riboflavina, Riboflavinum, Vitamin B2, Lactoflavin, Riboflavine, Vitamin G, Beflavin, Beflavine,
PubChem CID: 493570,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 83-88-5,
ChemIDplus: 83-88-5,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA04,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: C17H20N4O6,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2F4D60,
References:
Brain / Mental Clarity: KENNEDY, David O. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy–A Review. Nutrients, 2016, 8.2: 68. PMID:26828517.
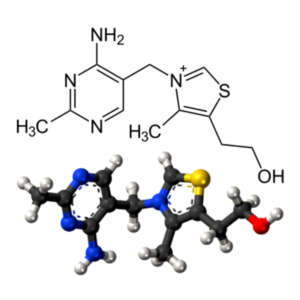
- Witamina B6 (Chlorowodorek Pirydoksyny) (C8H12ClNO3)
Witamina B6 (Chlorowodorek Pirydoksyny): Pyridoxine Hydrochloride, Pyridoxine HCl, Pyridoxol Hydrochloride, Alestrol, Becilan, Benadon, Hexavibex, Hexermin, Aderoxin, PubChem CID: 6019, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 58-56-0, ChemIDplus: 58-56-0, WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA02, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 68Y4CF58BV, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS264CB0-1.
- Witamina B6 (Pirydoksyna) (C8H11NO3)
Wymagana do biosyntezy kilku neuroprzekaźników, w tym dopaminy, serotoniny i GABA. CILTEP zawiera metabolicznie aktywną formę witaminy B-6 (pirydoksal-5-fosforan), aby zapewnić optymalne funkcje poznawcze. Chociaż wszystkie witaminy z grupy B są niezbędne, witamina B6 jest jedną z najważniejszych. Odgrywa rolę w ponad 100 reakcjach enzymatycznych w organizmie, przede wszystkim w metabolizmie ważnych aminokwasów i białek. Bierze udział w syntezie hemoglobiny i aktywuje w komórkach gen smukłości SIRT. Witamina B6 dba o prawidłowy metabolizm energetyczny. Reguluje pracę układu hormonalnego i pozwala zachować wewnętrzną równowagę. Witamina B6 (Pirydoksyna): Pyridoxine, Gravidox, Pyridoxol, Vitamin B6,
Witamina B6 (Pirydoksyna): Pyridoxine, Gravidox, Pyridoxol, Vitamin B6,
PubChem CID: 1054,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 65-23-6,
ChemIDplus: 65-23-6,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA02,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: KV2JZ1BI6Z,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS264CB0,
References:
Vitamins: SPINNEKER, A.; et al. Vitamin B6 Status, Deficiency and Its Consequences – An Overview. Nutricion hospitalaria, 2007, 22.1: 7-24. PMID:17260529, AHMAD, Iqbal; et al. Vitamin B 6: Deficiency diseases and methods of analysis. Pakistan journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 2013, 26.5: . PMID:24035968,
Weight Loss: NOVIN, Zahra Shakibay; GHAVAMZADEH, Saeed; MEHDIZADEH, Alireza The Weight Loss Effects of Branched Chain Amino Acids and Vitamin B6: A Randomized Controlled Trial on Obese and Overweight Women. International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research, 2019, 2019: . PMID:30841823,
Brain / Mental Clarity: BOURRE, Jean-Marie Effects of nutrients (in food) on the structure and function of the nervous system: update on dietary requirements for brain. Part 1: micronutrients. Journal of Nutrition Health and Aging, 2006, 10.5: 377. PMID:17066209, RAMOS, Rúben J.; et al. Vitamin B6 Is Essential for Serine De Novo Biosynthesis. Journal of inherited metabolic disease, 2017, 40.6: 883-891. PMID:28801717,
Stress / Relaxation: POUTEAU, Etienne; et al. Superiority of Magnesium and Vitamin B6 Over Magnesium Alone on Severe Stress in Healthy Adults With Low Magnesemia: A Randomized, Single-Blind Clinical Trial. PloS one, 2018, 13.12: e0208454. PMID:30562392, KELLY, Gregory S. Nutritional and Botanical Interventions to Assist With the Adaptation to Stress. Alternative medicine review: a journal of clinical therapeutic, 1999, 4.4: 249-265. PMID:10468649,
Menopause: MCCABE, Delia; et al. The Impact of Essential Fatty Acid, B Vitamins, Vitamin C, Magnesium and Zinc Supplementation on Stress Levels in Women: A Systematic Review. JBI database of systematic reviews and implementation reports, 2017, 15.2: 402-453. PMID:28178022.
- Witamina B7 (Biotyna) (C10H16N2O3S)
Biotyna jest zwykle kojarzona z włosami i paznokciami, ale pomaga również w procesie odchudzania. Będąc ważnym składnikiem enzymów, które działają w celu eliminacji tłuszczu, węglowodanów i innych substancji z organizmu, biotyna pomaga zapobiegać gromadzeniu tłuszczu przez nadmierne spożycie kalorii. Witamina B7 (Biotyna): Biotin, D-Biotin, Coenzyme R, Vitamin B7, Vitamin H,
Witamina B7 (Biotyna): Biotin, D-Biotin, Coenzyme R, Vitamin B7, Vitamin H,
PubChem CID: 171548,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 58-85-5,
ChemIDplus: 58-85-5,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA05,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 6SO6U10H04,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS269AD0.
- Witamina B9 (Kwas Foliowy, Folacyna) (C19H19N7O6)
 Witamina B9 (Kwas Foliowy, Folacyna): Folic Acid, Folacin, Pteroylglutamic Acid, Pteroylmonoglutamic Acid, Vitamin B9, Folate,
Witamina B9 (Kwas Foliowy, Folacyna): Folic Acid, Folacin, Pteroylglutamic Acid, Pteroylmonoglutamic Acid, Vitamin B9, Folate,
PubChem CID: 135398658,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 59-30-3,
ChemIDplus: 59-30-3,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: B03BB01,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 935E97BOY8,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2673C0,
References:
Vitamins: OBEID, Rima; HOLZGREVE, Wolfgang; PIETRZIK, Klaus Is 5-methyltetrahydrofolate an Alternative to Folic Acid for the Prevention of Neural Tube Defects? Journal of perinatal medicine, 2013, 41.5: 469-483. PMID:23482308, SCAGLIONE, Francesco; PANZAVOLTA, Giscardo Folate, Folic Acid and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate Are Not the Same Thing. Xenobiotica, 2014, 44.5: 480-488. PMID:24494987,
Brain / Mental Clarity: GUILLAND, Jean-Claude; AIMONE-GASTIN, Isabelle Vitamin B9. La Revue du praticien, 2013, 63.8, 1079: 1081-4. PMID:24298825, BOURRE, Jean-Marie Effects of nutrients (in food) on the structure and function of the nervous system: update on dietary requirements for brain. Part 1: micronutrients. Journal of Nutrition Health and Aging, 2006, 10.5: 377. PMID:17066209.
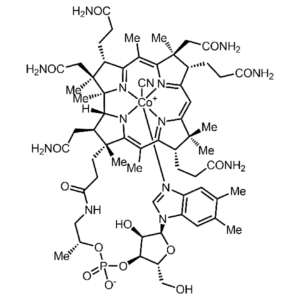
- Witamina B12 (Kobalamina, Cyjanokobalamina) (C63H88CoN14O14P)
 Witamina B12 (Kobalamina, Cyjanokobalamina): Cyanocobalamin, Vitamin B12, Cobalamin, Crystamine, Anacobin,
Witamina B12 (Kobalamina, Cyjanokobalamina): Cyanocobalamin, Vitamin B12, Cobalamin, Crystamine, Anacobin,
PubChem CID: 5311498,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 68-19-9,
ChemIDplus: 68-19-9,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: B03BA01,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: P6YC3EG204,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS30D400,
References:
Brain / Mental Clarity: SMITH, A. David; WARREN, Martin J.; REFSUM, Helga Vitamin B12. In: Advances in food and nutrition research. Academic Press, 2018, 2018: 215-279. PMID:29477223, TANGNEY, C. C.; AGGARWAL, N. T.; LI, H.; WILSON, R. S.; DECARLI, C.; EVANS, D. A.; MORRIS, M. C. Vitamin B12, cognition, and brain MRI measures: a cross-sectional examination. Neurology, 2011, 77.13: 1276-1282. PMID:21947532,
Stress / Relaxation: KELLY, Gregory S. Nutritional and Botanical Interventions to Assist With the Adaptation to Stress. Alternative medicine review: a journal of clinical therapeutic, 1999, 4.4: 249-265. PMID:10468649. - Witamina B1 (Azotan Tiaminy) (C12H17N5O4S)
- Witamina B1 (Tiamina/Aneurina) (C12H17N4OS+)
- Soja (Glycine Max)
Izolat białka sojowego spala tłuszcz, jest źródłem energii dla organizmu (czynnie spala podskórny tłuszcz). Species: Glycine Max, Family: Fabaceae, European Medicines Agency: EMA: Lecithinum Ex Soya, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IHA826E0, References: Weight Loss: SHARMANOV, TSh; KADYROVA, RKh; SALKHANOV, B. A. The use of a soy protein isolate in the diet therapy of patients with alimentary obesity. Voprosy pitaniia, 1990, 2: 27-29. PMID:2378098, TAHAVORGAR, Atefeh; et al. Whey protein preloads are more beneficial than soy protein preloads in regulating appetite, calorie intake, anthropometry, and body composition of overweight and obese men. Nutrition research, 2014, 34.10: 856-861. PMID:25277886.
- Izoflawony Sojowe
Szczegółowe informacje na temat składników suplementu Doppelherz aktiv Aktiv-Meno
| Doppelherz aktiv Aktiv-Meno | ||
|---|---|---|
| Składnik | 1 tabletka | % RWS* |
| Koncentrat sojowy, w tym: izoflawony sojowe: |
125 mg 50 mg |
– – |
| Wapń | 500 mg | 63% |
| Witamina D | 5 µg | 100% |
| Tiamina (witamina B1) | 1,40 mg | 127% |
| Ryboflawina (witamina B2) | 1,60 mg | 114% |
| Witamina B6 | 2 mg | 143% |
| Witamina B12 | 3 µg | 120% |
| Biotyna | 150 µg | 300% |
| Kwas foliowy (witamina B9) | 400 µg | 200% |
Szczegóły dotyczące składu
Dla kogo przeznaczony jest suplement Doppelherz aktiv Aktiv-Meno?
Osoby, które mogą przyjmować suplement “Doppelherz aktiv Aktiv-Meno” firmy QUEISSER:
- Dorośli
- Seniorzy
Dawkowanie suplementu Doppelherz aktiv Aktiv-Meno
- Dorośli: 1 tabletka dziennie po posiłku. Tabletkę można dzielić.
Uwaga
- Nie należy przekraczać zalecanej dziennej porcji.
- Dla utrzymania prawidłowego stanu zdrowia należy stosować zróżnicowaną dietę i prowadzić zdrowy tryb życia.
- Suplement diety nie może być stosowany jak substytut (zamiennik) zróżnicowanej diety.
- Przechowywać w temperaturze pokojowej.
- Chronić od światła i wilgoci.
- Przechowywać w sposób niedostępny dla małych dzieci.
Zobacz również: Przepisy prawa regulujące znakowanie suplementów diety
Suplementy diety podobne do Doppelherz aktiv Aktiv-Meno
Suplement diety Doppelherz aktiv Aktiv-Meno jest dostepny w Polsce. Zawiera takie składniki jak: B Vitamins, Calcium, Soya Bean, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B12, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B7, Vitamin B9, Vitamin D and Vitamin D3.




























































Leave a Reply