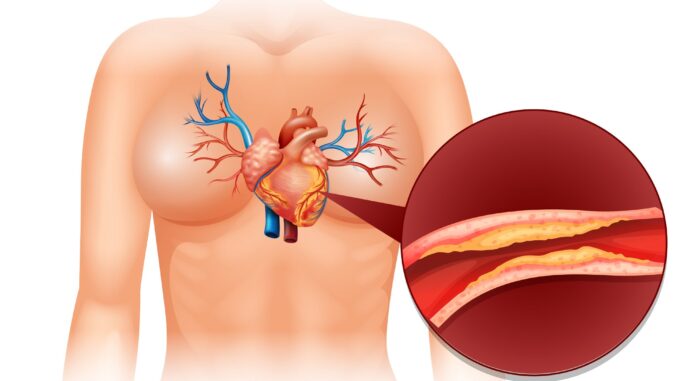
Many people have difficulty maintaining normal cholesterol levels, which is related to the current lifestyle containing: improper nutrition, insufficient physical activity, fast life, stress, genetic factors, and even environmental pollution such as smog. Trivialising this problem may result in heart and cardiovascular disease. The condition for normalizing the level of cholesterol in the blood is to combine a well-balanced diet with the use of supplementation and physical activity.
It is known that cholesterol cannot be eliminated from the diet because it is essential for proper functioning. However, high cholesterol can be dangerous and leads to many health complications. The supplements you can find here contain natural ingredients such as polyunsaturated fats from fish oil but also vegetable ingredients and herbs supporting a proper level of cholesterol in the blood.