The properties of Borago
Borage (Borago officinalis) is an annual herb which is cultivated for medicinal and culinary uses, although it is commercially cultivated for borage seed oil. Borage seed oil is the plant rich in the gamma-linolenic acid (26%-38%) which is used as dietary or food supplement. Other than seed oil it contains a lot of fatty acids such as linoleic acid (35%-38%), oleic acid (16%-20%), palmitic acid (10%-11%), stearic acid (3.5%-4.5%), eicosenoic acid (3.5%-5.5%) and erucic acid (1.5%-3.5%)(1066).
Traditionally, Borago Officinalis has been used in hyperactive gastrointestinal, respiratory and cardiovascular disorders, such as gastrointestinal (colic, cramps, diarrhea), airways (asthma, bronchitis), cardiovascular, (cardiotonic, antihypertensive and blood purifier), urinary (diuretic and kidney/bladder disorders).
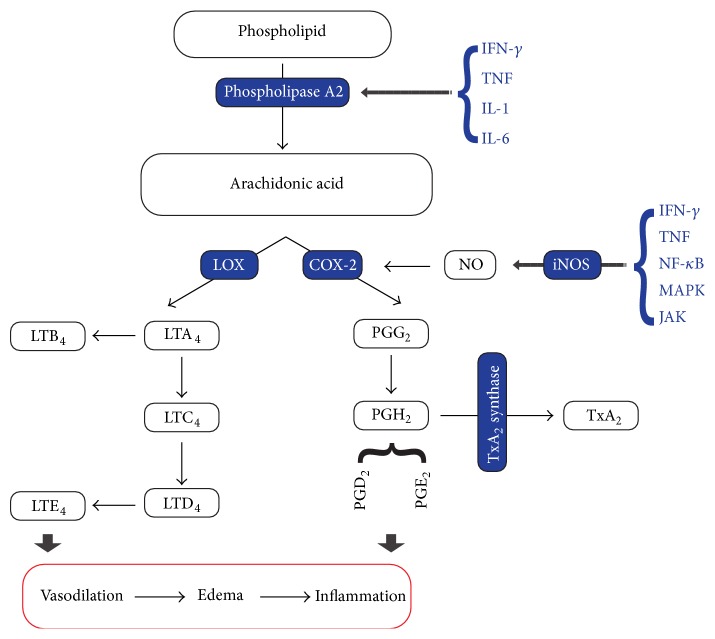
This plant is a rich source of gamma linoleic acid (GLA), which contains 25% of GLA, by elevating prostaglandin-E (PGE) level that leads to cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) augmentation; GLA could count as a strong suppressor of TNF-α. The mechanism mentioned above can clarify the anti-inflammatory effect of borage oil in rheumatoid arthritis (RA)(1070). Regarding this pathway, borage has contraindication during pregnancy because of the miscarriage risk. Antirheumatoid arthritis's potential of borage seed oil was assessed in 2 RCT as follows: in the first study, 1.4 g/day borage seed oil has been compared with placebo in RA patients; 36.8% amelioration occurred in the treatment group at the end of 6-month therapy. In the second study, 2.8 g/day of borage seed oil was taken by patients during 6 months; at the end of treatment, the amelioration percent of RA manifestation was noticeable: 64% in the treatment group compared with 21% in the control group(1071). Likewise, the anti-inflammatory effect of borage oil was tested in patients with atopic dermatitis. 12 clinical trials were performed to evaluate the effectiveness of this herb in ameliorating in atopic dermatitis. 5 of those have proved the anti-inflammatory effect and 2 of those have recorded improving in some patients, although in the rest 5 trials there has not been any observation for remission(1072).(1069)