The properties of Garlic
Garlic (Allium Sativum) is one of the most researched and best-selling herbal products on the market.
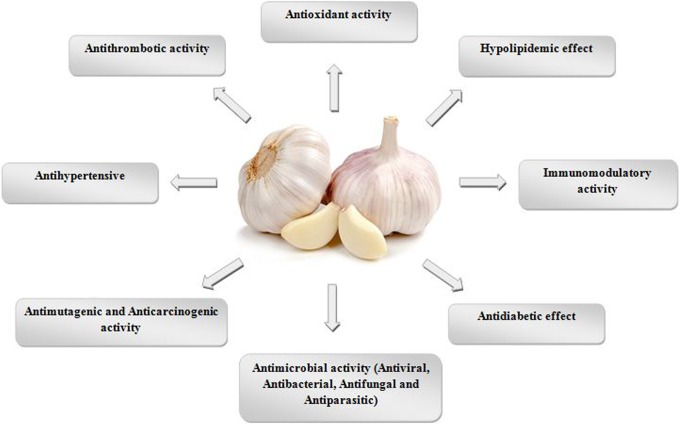
Garlic's properties result from a combination of variety biologically active substances which all together are responsible for its curative effect. The compounds contained in garlic synergistically influence each other so that they can have different effects. The active ingredients of garlic include enzymes (e.g. alliinase), sulfur-containing compounds such as alliin and compounds produced enzymatically from alliin (e.g. allicin). There is a lot of variation among garlic products sold for medicinal purposes. The concentration of Allicin (main active ingredient) and the source of garlic's distinctive odor depend on processing method.
It's documented that products obtained even without allicin such as aged garlic extract (AGE), have a clear and significant biological effect in immune system improvement, treatment of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, liver and other areas.
Some products have a coating (enteric coating) to protect them against attack by stomach acids. Clinically, garlic has been evaluated for a number of purposes, including treatment of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, cold or the prevention of atherosclerosis and the development of tumors. Many available publications indicates possible antibacterial, anti-hypertensive and anti-thrombotic properties of garlic(914).
Garlic contains diverse bioactive compounds, such as allicin, alliin, diallyl sulfide, diallyl disulfide, diallyl trisulfide, ajoene, and S-allyl-cysteine.
Overall, garlic is an excellent natural source of bioactive sulfur-containing compounds and has promising applications in the development of functional foods or nutraceuticals for the prevention and management of certain diseases(916).