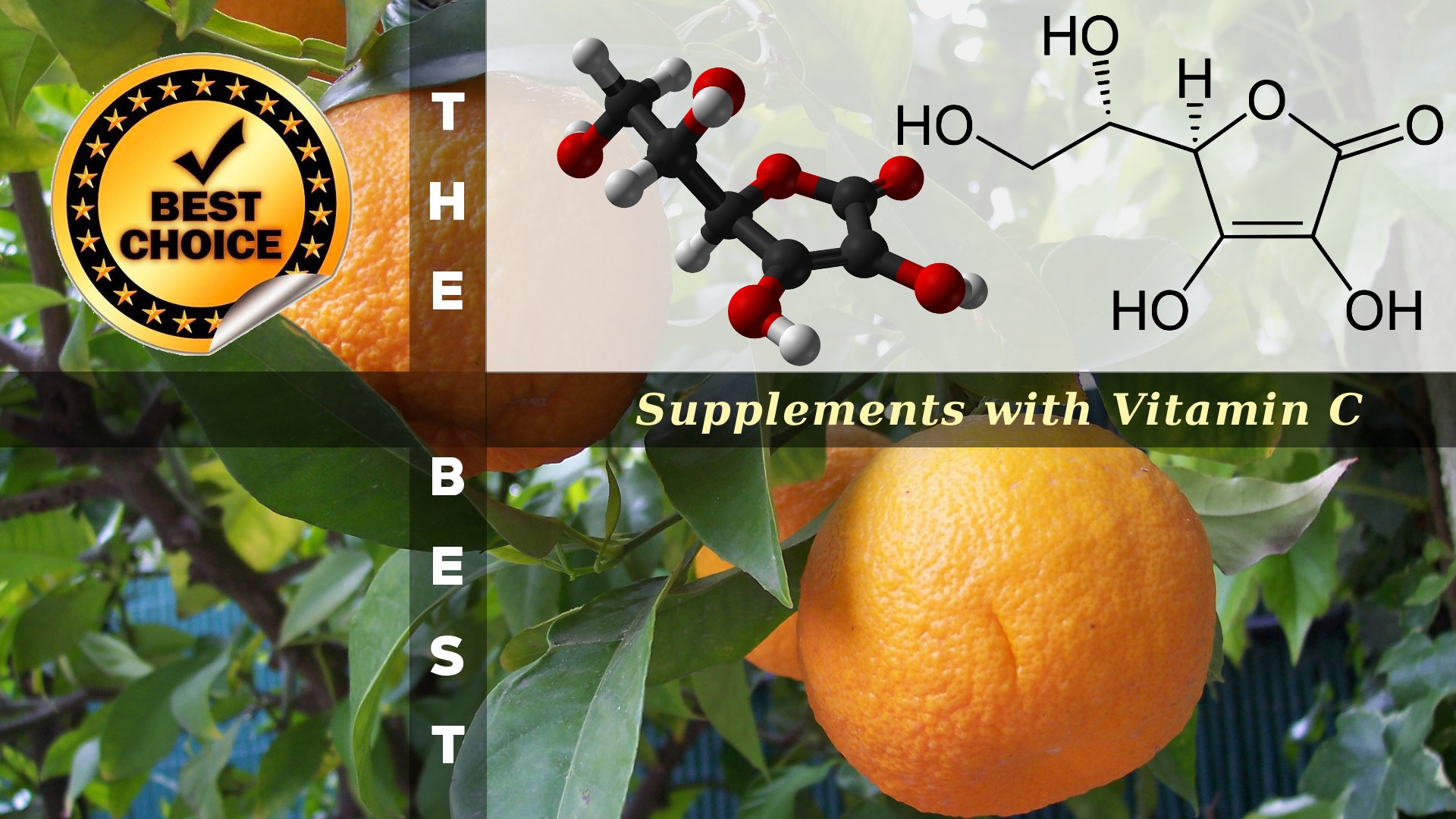
The properties of Vitamin C
Supports the body in the production of collagen to ensure the proper functioning of veins, arteries and small blood vessels. Like all 8 B vitamins, vitamin C aids in protein metabolism. This means it not only provides your body with necessary proteins, but does so while blocking the synthesis of proteins known to cause infection and inflammation. That means if you go to the gym often, vitamin C can make it easier for you to recover after training.A study revealed that those with adequate vitamin C intake oxidize 30% more fat during exercise than those with low vitamin C, meaning people without enough vitamin C may find it harder to lose body fat.
Vitamin C – plays an essential role skin regeneration. Studies have confirmed that vitamin C can reduce irritation and redness associated with acne scars and acne. It also rebuilds damaged collagen, which is responsible for skin elasticity.
Vitamin C supports the body in the production of collagen to ensure the proper functioning of veins, arteries and small blood vessels.
It plays an important role in bone formation, wound healing and the maintenance of healthy gums. Vitamin C plays an important role in a number of metabolic functions including the activation of the B vitamin, folic acid, the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids and the conversion of the amino acid, tryptophan, to the neurotransmitter, serotonin.
It is an antioxidant that protects body from free radical damage. It is used as therapeutic agent in many diseases and disorders.
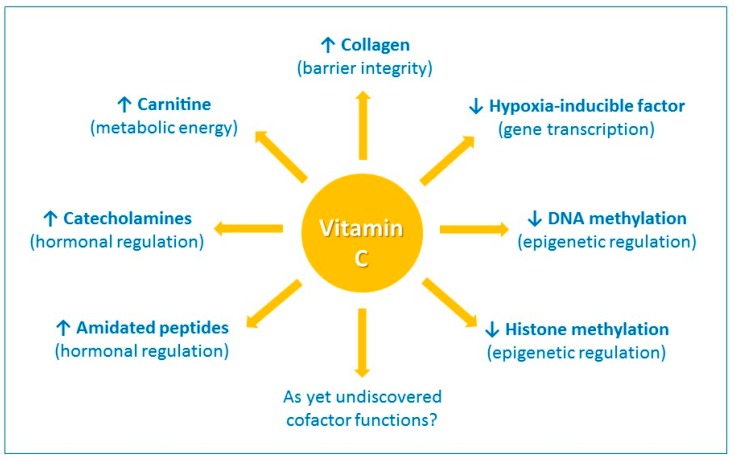
Vitamin C and Immune Function
Vitamin C is an essential micronutrient for humans, with pleiotropic functions related to its ability to donate electrons. It is a potent antioxidant and a cofactor for a family of biosynthetic and gene regulatory enzymes. Vitamin C contributes to immune defense by supporting various cellular functions of both the innate and adaptive immune system. Vitamin C supports epithelial barrier function against pathogens and promotes the oxidant scavenging activity of the skin, thereby potentially protecting against environmental oxidative stress. Vitamin C accumulates in phagocytic cells, such as neutrophils, and can enhance chemotaxis, phagocytosis, generation of reactive oxygen species, and ultimately microbial killing. It is also needed for apoptosis and clearance of the spent neutrophils from sites of infection by macrophages, thereby decreasing necrosis/NETosis and potential tissue damage(859).
Vitamin C and Hair Loss
Vitamin C is reducing mediator necessary for collagen fiber synthesis through hydroxylation of lysine and proline. Vitamin C plays an essential role in the intestinal absorption of iron due to its chelating and reducing effect, assisting iron mobilization and intestinal absorption. Therefore, vitamin C intake is important in people with hair loss associated with iron deficiency.Humans are naturally deficient in an enzyme called l-gulonolactone oxidase that is required for vitamin C synthesis, and should therefore take vitamin C through their diet(1173).