

Solgar’s KOF-K certification #K-1250.
B-Complex “100”, 100 Vegetable Capsules (Solgar) – Ingredients
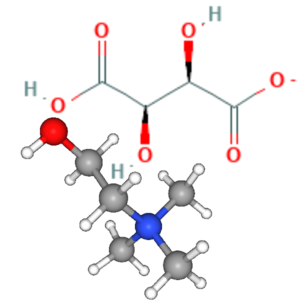
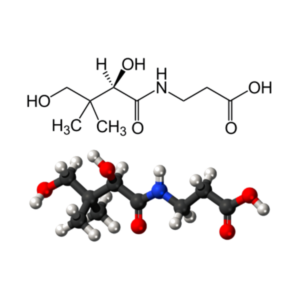
- Choline
- Choline Bitartrate (C9H19NO7)
 Choline Bitartrate: Choline Bitartrate, Choline Tartrate, Choline-Bitartrate, Cholini Bitartras, Cholinibitatratis,
Choline Bitartrate: Choline Bitartrate, Choline Tartrate, Choline-Bitartrate, Cholini Bitartras, Cholinibitatratis,
PubChem CID: 6900,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 87-67-2,
ChemIDplus: 87-67-2,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS32CFD0-1.
- Choline Bitartrate (C9H19NO7)
- Vitamin B
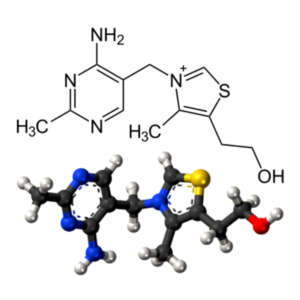
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine/aneurine) (C12H17N4OS+)
 Vitamin B1 (thiamine/aneurine): Thiamine, Vitamin B1, Aneurin, Antiberiberi Factor, Thiadoxine, Betaxin, Thiamin,
Vitamin B1 (thiamine/aneurine): Thiamine, Vitamin B1, Aneurin, Antiberiberi Factor, Thiadoxine, Betaxin, Thiamin,
PubChem CID: 1130,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 70-16-6,
ChemIDplus: 70-16-6,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11DA01,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: X66NSO3N35,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2A6B60,
References:
Brain / Mental Clarity: BOURRE, Jean-Marie Effects of nutrients (in food) on the structure and function of the nervous system: update on dietary requirements for brain. Part 1: micronutrients. Journal of Nutrition Health and Aging, 2006, 10.5: 377. PMID:17066209, KENNEDY, David O. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy–A Review. Nutrients, 2016, 8.2: 68. PMID:26828517.
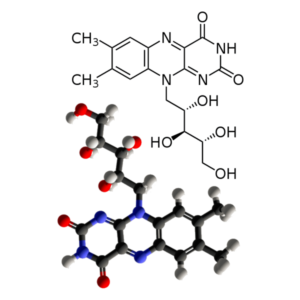
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) (C17H20N4O6)
 Vitamin B2 (riboflavin): Riboflavin, Riboflavina, Riboflavinum, Vitamin B2, Lactoflavin, Riboflavine, Vitamin G, Beflavin, Beflavine,
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin): Riboflavin, Riboflavina, Riboflavinum, Vitamin B2, Lactoflavin, Riboflavine, Vitamin G, Beflavin, Beflavine,
PubChem CID: 493570,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 83-88-5,
ChemIDplus: 83-88-5,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA04,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: C17H20N4O6,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2F4D60,
References:
Brain / Mental Clarity: KENNEDY, David O. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy–A Review. Nutrients, 2016, 8.2: 68. PMID:26828517.
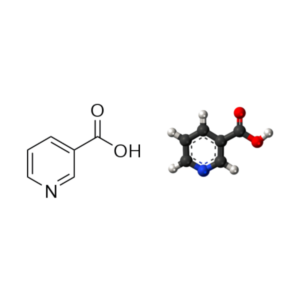
- Vitamin B3 (niacin/nicotinic acid) (C6H5NO2 or HOOC5H4N or C5H4NCOOH)
 Vitamin B3 (niacin/nicotinic acid): Nicotinic Acid, Vitamin B3, Vitamin PP, Niacin, Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid, 3-Pyridinecarboxylic Acid,
Vitamin B3 (niacin/nicotinic acid): Nicotinic Acid, Vitamin B3, Vitamin PP, Niacin, Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid, 3-Pyridinecarboxylic Acid,
PubChem CID: 938,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 59-67-6,
ChemIDplus: 59-67-6,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: C04AC01,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 25X51I8RD4,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS30FB10,
References:
Brain / Mental Clarity: KENNEDY, David O. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy–A Review. Nutrients, 2016, 8.2: 68. PMID:26828517.
- Vitamin B5 (D-Pantothenic Acid) (C9H17NO5)
 Vitamin B5 (D-Pantothenic Acid): D-Pantothenic Acid, Vitamin B5, Pantothenic Acid, Pantothenate,
Vitamin B5 (D-Pantothenic Acid): D-Pantothenic Acid, Vitamin B5, Pantothenic Acid, Pantothenate,
PubChem CID: 6613,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 79-83-4,
ChemIDplus: 79-83-4,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA31,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 19F5HK2737,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS26C1E0,
References:
Brain / Mental Clarity: KENNEDY, David O. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy–A Review. Nutrients, 2016, 8.2: 68. PMID:26828517,
Stress / Relaxation: KELLY, Gregory S. Nutritional and Botanical Interventions to Assist With the Adaptation to Stress. Alternative medicine review: a journal of clinical therapeutic, 1999, 4.4: 249-265. PMID:10468649.
- Vitamin B5 (Calcium Pantothenate) (C9H17CaNO5+2)
Vitamin B5 (Calcium Pantothenate): Calcium Pantothenate, Panthoject, Calpanate, PubChem CID: 11777341, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 137-08-6, ChemIDplus: 137-08-6, WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA31, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 568ET80C3D, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS26C1E0-1.
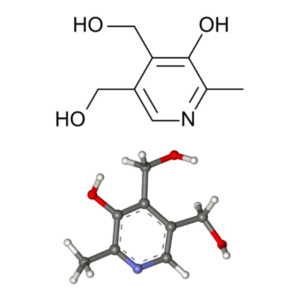
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) (C8H11NO3)
Required for the biosynthesis of several neurotransmitters including dopamine, serotonin, and GABA. CILTEP features the metabolically active form of vitamin B-6 (Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate) to ensure optimal cognitive function. Low dietary intake or reduced blood concentrations of vitamin B6 is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Pyridoxine, Gravidox, Pyridoxol, Vitamin B6,
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine): Pyridoxine, Gravidox, Pyridoxol, Vitamin B6,
PubChem CID: 1054,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 65-23-6,
ChemIDplus: 65-23-6,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA02,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: KV2JZ1BI6Z,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS264CB0,
References:
Vitamins: SPINNEKER, A.; et al. Vitamin B6 Status, Deficiency and Its Consequences – An Overview. Nutricion hospitalaria, 2007, 22.1: 7-24. PMID:17260529, AHMAD, Iqbal; et al. Vitamin B 6: Deficiency diseases and methods of analysis. Pakistan journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 2013, 26.5: . PMID:24035968,
Cardiovascular Support: FRISO, Simonetta; et al. Vitamin B6 and Cardiovascular Disease. In: Water Soluble Vitamins. Springer, Dordrecht, 2012, 56: 265-290. PMID:22116704, JEON, Jimin; PARK, Kyong Dietary Vitamin B 6 Intake Associated With a Decreased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients, 2019, 11.7: 1484. PMID:31261898,
Hair / Skin Care: COBURN, Stephen P.; et al. Cutaneous Metabolism of Vitamin B-6. Journal of investigative dermatology, 2003, 120.2: 292-300. PMID:12542535,
Brain / Mental Clarity: BOURRE, Jean-Marie Effects of nutrients (in food) on the structure and function of the nervous system: update on dietary requirements for brain. Part 1: micronutrients. Journal of Nutrition Health and Aging, 2006, 10.5: 377. PMID:17066209, RAMOS, Rúben J.; et al. Vitamin B6 Is Essential for Serine De Novo Biosynthesis. Journal of inherited metabolic disease, 2017, 40.6: 883-891. PMID:28801717,
Stress / Relaxation: POUTEAU, Etienne; et al. Superiority of Magnesium and Vitamin B6 Over Magnesium Alone on Severe Stress in Healthy Adults With Low Magnesemia: A Randomized, Single-Blind Clinical Trial. PloS one, 2018, 13.12: e0208454. PMID:30562392, KELLY, Gregory S. Nutritional and Botanical Interventions to Assist With the Adaptation to Stress. Alternative medicine review: a journal of clinical therapeutic, 1999, 4.4: 249-265. PMID:10468649.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine Hydrochloride) (C8H12ClNO3)
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine Hydrochloride): Pyridoxine Hydrochloride, Pyridoxine HCl, Pyridoxol Hydrochloride, Alestrol, Becilan, Benadon, Hexavibex, Hexermin, Aderoxin, PubChem CID: 6019, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 58-56-0, ChemIDplus: 58-56-0, WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA02, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 68Y4CF58BV, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS264CB0-1, References: Cardiovascular Support: MIDTTUN, Øivind; et al. Low Plasma Vitamin B-6 Status Affects Metabolism Through the Kynurenine Pathway in Cardiovascular Patients With Systemic Inflammation. The Journal of nutrition, 2011, 141.4: 611-617. PMID:21310866, ULVIK, Arve; et al. Substrate Product Ratios of Enzymes in the Kynurenine Pathway Measured in Plasma as Indicators of Functional Vitamin B-6 Status. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 2013, 98.4: 934-940. PMID:24004893.
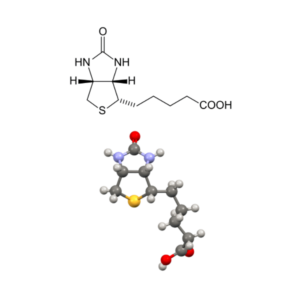
- Vitamin B7 (biotin) (C10H16N2O3S)
 Vitamin B7 (biotin): Biotin, D-Biotin, Coenzyme R, Vitamin B7, Vitamin H,
Vitamin B7 (biotin): Biotin, D-Biotin, Coenzyme R, Vitamin B7, Vitamin H,
PubChem CID: 171548,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 58-85-5,
ChemIDplus: 58-85-5,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA05,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 6SO6U10H04,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS269AD0.
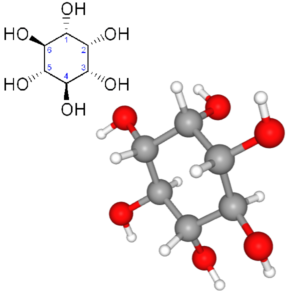
- Vitamin B8 (Inositol) (C6H12O6)
 Vitamin B8 (Inositol): Inositol, Scyllitol, Myoinosite, Quercinitol, Meat Sugar, Vitamin B8, Myoinositol, Scyllo-Inositol, Myo-Inositol, Muco-Inositol, Mesoinositol, Allo-Inositol,
Vitamin B8 (Inositol): Inositol, Scyllitol, Myoinosite, Quercinitol, Meat Sugar, Vitamin B8, Myoinositol, Scyllo-Inositol, Myo-Inositol, Muco-Inositol, Mesoinositol, Allo-Inositol,
PubChem CID: 892,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 87-89-8,
ChemIDplus: 87-89-8,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11HA07,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 4L6452S749,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS3B3440,
References:
Brain / Mental Clarity: FISHER, Stephen K.; NOVAK, James E.; AGRANOFF, Bernard W. Inositol and higher inositol phosphates in neural tissues: homeostasis, metabolism and functional significance. Journal of neurochemistry, 2002, 82.4: 736-754. PMID:12358779.
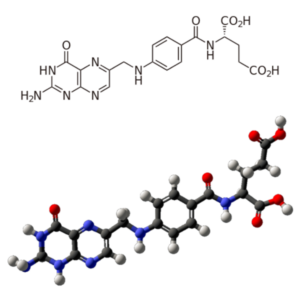
- Vitamin B9 (folic acid, folacin) (C19H19N7O6)
 Vitamin B9 (folic acid, folacin): Folic Acid, Folacin, Pteroylglutamic Acid, Pteroylmonoglutamic Acid, Vitamin B9, Folate,
Vitamin B9 (folic acid, folacin): Folic Acid, Folacin, Pteroylglutamic Acid, Pteroylmonoglutamic Acid, Vitamin B9, Folate,
PubChem CID: 135398658,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 59-30-3,
ChemIDplus: 59-30-3,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: B03BB01,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 935E97BOY8,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2673C0,
References:
Vitamins: OBEID, Rima; HOLZGREVE, Wolfgang; PIETRZIK, Klaus Is 5-methyltetrahydrofolate an Alternative to Folic Acid for the Prevention of Neural Tube Defects? Journal of perinatal medicine, 2013, 41.5: 469-483. PMID:23482308, SCAGLIONE, Francesco; PANZAVOLTA, Giscardo Folate, Folic Acid and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate Are Not the Same Thing. Xenobiotica, 2014, 44.5: 480-488. PMID:24494987,
Brain / Mental Clarity: GUILLAND, Jean-Claude; AIMONE-GASTIN, Isabelle Vitamin B9. La Revue du praticien, 2013, 63.8, 1079: 1081-4. PMID:24298825, BOURRE, Jean-Marie Effects of nutrients (in food) on the structure and function of the nervous system: update on dietary requirements for brain. Part 1: micronutrients. Journal of Nutrition Health and Aging, 2006, 10.5: 377. PMID:17066209.
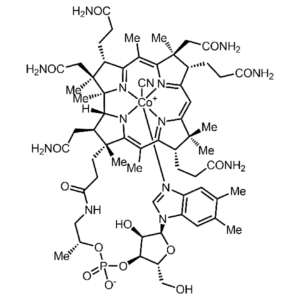
- Vitamin B12 (cobalamin, cyanocobalamin) (C63H88CoN14O14P)
 Vitamin B12 (cobalamin, cyanocobalamin): Cyanocobalamin, Vitamin B12, Cobalamin, Crystamine, Anacobin,
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin, cyanocobalamin): Cyanocobalamin, Vitamin B12, Cobalamin, Crystamine, Anacobin,
PubChem CID: 5311498,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 68-19-9,
ChemIDplus: 68-19-9,
WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: B03BA01,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: P6YC3EG204,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS30D400,
References:
Brain / Mental Clarity: SMITH, A. David; WARREN, Martin J.; REFSUM, Helga Vitamin B12. In: Advances in food and nutrition research. Academic Press, 2018, 2018: 215-279. PMID:29477223, TANGNEY, C. C.; AGGARWAL, N. T.; LI, H.; WILSON, R. S.; DECARLI, C.; EVANS, D. A.; MORRIS, M. C. Vitamin B12, cognition, and brain MRI measures: a cross-sectional examination. Neurology, 2011, 77.13: 1276-1282. PMID:21947532,
Stress / Relaxation: KELLY, Gregory S. Nutritional and Botanical Interventions to Assist With the Adaptation to Stress. Alternative medicine review: a journal of clinical therapeutic, 1999, 4.4: 249-265. PMID:10468649. - Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) (C17H20N4O6)
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine/aneurine) (C12H17N4OS+)
| Supplement Facts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name: | B-Complex “100”, 100 Vegetable Capsules | |
| Serving Size: | 1 Vegetable Capsule | |
| Amount Per Serving | %DV | |
| Thiamin (Vitamin B1) (Thiamin Mononitrate) | 100 mg | 8,333% |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 100 mg | 7,692% |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) (NIACINAMIDE) | 100 mg | 625% |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine Hcl) | 100 mg | 5,882% |
| Folate | 666 mcg DFE (400 McG Folic Acid) | 167% |
| Vitamin B12 (CYANOCOBALAMIN) | 100 mcg | 4,167% |
| Biotin (D-BIOTIN) | 100 mcg | 333% |
| Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) (D-Calcium Pantothenate) | 100 mg | 2,000% |
| Choline (Choline Bitartrate) | 20 mg | 4% |
| Inositol | 100 mg | ××) |
| ××) Daily Value (DV) not established. | ||
| Manufacturer: | Solgar |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer Code: | 01150 |
| UPC Code (gtin12): | 033984011502 |
| Package Quantity | |
| Count | 100 |
Other ingredients
Vegetable cellulose, vegetable magnesium stearate, silica.
Free of: Gluten, wheat, dairy, soy, yeast, sugar, sodium, artificial flavor, sweetener, preservatives and color.
B-Complex “100”, 100 Vegetable Capsules – Suggested Use
Adults, take one (1) vegetable capsule daily, preferably with a meal or directed by a healthcare practitioner.
| Recommended Intake | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dose Unit | Dose Value | Frequency | Target Population |
| capsule | 1 | daily | adults |
Warnings
- Not intended for use by pregnant or nursing women. If you are taking any medications or have any medical condition, please consult your healthcare practitioner before taking any dietary supplement. Discontinue use and consult your healthcare practitioner if any adverse reactions occur. Keep out of reach of children. Store at room temperature. Do not use if outer bottle seal is missing or damaged.
Dietary supplements similar to B-Complex “100”, 100 Vegetable Capsules (Solgar)
The B-Complex “100”, 100 Vegetable Capsules (Solgar) dietary supplement is available in Croatia and many others countries around the world. In Croatia this supplement contains: B Vitamins, Choline, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B12, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B5, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B7, Vitamin B8 and Vitamin B9 in its composition.




























































Leave a Reply