The properties of Vitamin B5
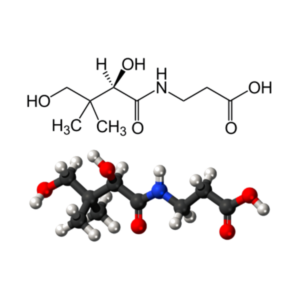
Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid C9H17NO5). Pantothenic acid helps your body metabolize food into energy while assisting your liver in metabolizing toxins that can stall your weight loss efforts.
Recommended Daily Allowance
Vitamin B5 – Recommended Daily Allowance: 5 mg.
Symptoms of Deficiency
Numbness/burning sensations in extremities, dermatitis, diarrhoea.
Dietary Sources
Good Dietary Sources of Vitamin B5:
- meat,
- whole grain cereals,
- broccoli.
Vitamin B5 and the Brain
Pantothenic acid is an essential nutrient that supports an important neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. The latter is sometimes called ‘the memory chemical’ because of the role it plays in brain function.
This vitamin is a substrate for the synthesis of the ubiquitous coenzyme A (CoA). Beyond its role in oxidative metabolism, CoA contributes to the structure and function of brain cells via its involvement in the synthesis of cholesterol, amino acids, phospholipids, and fatty acids. Of particular relevance, pantothenic acid, via CoA, is also involved in the synthesis of multiple neurotransmitters and steroid hormones(1262).
Brain Specific Symptoms of Deficiency
Encephalopathy, behaviour change, demyelination.