

Each serving may also have the following naturally occurring amounts of polyunsaturated fats and monounsaturated fats: Omega-3 [Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA) 45%; Omega-6 [Linoleic Acid and Gamma Linolenic Acid (GLA)] 26.5%; Omega-9 [Oleic Acid] 17.5%; Other (short chain fatty acids, saturated fats, phospholipids, etc) 11%
Omega 3-6-9, 1000 mg, 250 Softgels (Now Foods) – Ingredients
- Fish Oil
Fish oil is recommended for the management of hypertriglyceridemia and to prevent secondary cardiovascular disorders. Fish oil is a major source of ω-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Clinical studies suggest that fish oil not only prevents the incidence of detrimental cardiovascular events, but also lowers the cardiovascular mortality rate. Fish Oil: Fish Oil,
Fish Oil: Fish Oil,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISC99190,
References:
Cardiovascular Support: BALAKUMAR, Pitchai; TANEJA, Gaurav Fish Oil and Vascular Endothelial Protection: Bench to Bedside. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2012, 53.2: 271-279. PMID:22584102.
- Omega-3 Acids
Omega-3 Fatty acids benefit multiple risk factors including blood pressure, blood vessel function, heart function and blood lipids, and they have antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative actions. Supplementation with Omega-3 (ω3) fatty acids is recommended in individuals with elevated blood triglyceride levels and patients with coronary heart disease. This family of polyunsaturated fatty acids exerts major alterations on the activation of cells from both the innate and the adaptive immune system. EPA and DHA give rise to newly discovered resolvins which are anti-inflammatory and inflammation resolving.
Omega-3 Acids: Omega-3 Acids, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS317040, References: Immune: GUTIéRREZ, Saray; SVAHN, Sara L.; JOHANSSON, Maria E. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells. International journal of molecular sciences, 2019, 20.20: 5028. PMID:31614433, CALDER, Philip C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2017, 45.5: 1105-1115. PMID:28900017, Cardiovascular Support: MORI, Trevor A. Marine OMEGA-3 Fatty Acids in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Fitoterapia, 2017, 123: 51-58. PMID:28964873, JAIN, A. P.; AGGARWAL, K. K.; ZHANG, P. Y. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2015, 19.3: 441-5. PMID:25720716.
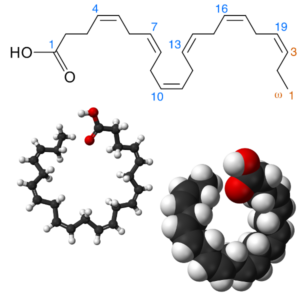
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (C22H32O2)
DHA inhibits the development of inflammation in endothelial cells, alters the function and regulation of vascular biomarkers, and reduces cardiovascular risk. Docosahexaenoic Acid: Docosahexaenoic Acid, DHA, Doconexent, Cervonic acid,
Docosahexaenoic Acid: Docosahexaenoic Acid, DHA, Doconexent, Cervonic acid,
PubChem CID: 445580,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 6217-54-5,
ChemIDplus: 6217-54-5,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: ZAD9OKH9JC,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS3567E0,
References:
Immune: GUTIéRREZ, Saray; SVAHN, Sara L.; JOHANSSON, Maria E. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells. International journal of molecular sciences, 2019, 20.20: 5028. PMID:31614433, CALDER, Philip C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2017, 45.5: 1105-1115. PMID:28900017,
Cardiovascular Support: YAMAGATA, Kazuo Docosahexaenoic Acid Regulates Vascular Endothelial Cell Function and Prevents Cardiovascular Disease. Lipids in health and disease, 2017, 16.1: 118. PMID:28619112.
- Eicosapentaenoic Acid (C20H30O2)
The omega-3 fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has multiple actions potentially conferring cardiovascular benefit, including lowering serum triglyceride (TG) and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) levels and potentially reducing key steps in atherogenesis. Eicosapentaenoic Acid: Eicosapentaenoic Acid, EPA, Timnodonic Acid, Icosapent,
Eicosapentaenoic Acid: Eicosapentaenoic Acid, EPA, Timnodonic Acid, Icosapent,
PubChem CID: 446284,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 10417-94-4,
ChemIDplus: 10417-94-4,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: AAN7QOV9EA,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISBF7F70,
References:
Immune: GUTIéRREZ, Saray; SVAHN, Sara L.; JOHANSSON, Maria E. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells. International journal of molecular sciences, 2019, 20.20: 5028. PMID:31614433, CALDER, Philip C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2017, 45.5: 1105-1115. PMID:28900017,
Cardiovascular Support: GOLZARI, Mohammad Hassan; et al. Effect of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) Supplementation on Cardiovascular Markers in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 2018, 12.3: 411-415. PMID:29588138, BRINTON, Eliot A.; MASON, R. Preston Prescription omega-3 Fatty Acid Products Containing Highly Purified Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA). Lipids in health and disease, 2017, 16.1: 23. PMID:28137294. - Eicosapentaenoic Acid (C20H30O2)
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (C22H32O2)
- Pumpkin Seed Oil (Cucurbita Pepo)
 Species: Cucurbita Pepo,
Species: Cucurbita Pepo,
Family: Cucurbitaceae,
European Medicines Agency: EMA: Cucurbitae Semen,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IHB1C3D0.
- Omega-6 Acids
Supplementation of omega-6 fatty acids may be beneficial in people at high risk of myocardial infarction.
Omega-6 Acids: Omega-6 Acids, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISCB1830, References: Cardiovascular Support: HOOPER, Lee; et al. Omega-6 Fats for the Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2018, 7: CD011094. PMID:30019765, AL-KHUDAIRY, Lena; et al. Omega 6 Fatty Acids for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2015, 11: CD011094. PMID:26571451.
- Gamma-Linolenic Acid (C18H30O2)
Gamma-Linolenic Acid: Gamma-Linolenic Acid, GLA, Gamolenic Acid, Ligla, PubChem CID: 5280933, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 506-26-3, ChemIDplus: 506-26-3, WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: D11AX02, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 78YC2MAX4O, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISB08B50.
- Linoleic Acid (C18H32O2)
Linoleic Acid: Linoleic Acid, Linolic Acid, Telfairic Acid, Linoleate, PubChem CID: 5280450, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 60-33-3, ChemIDplus: 60-33-3, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 9KJL21T0QJ, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISC39E20. - Linoleic Acid (C18H32O2)
- Omega-9 Acids
Omega-9 Acids: Omega-9 Acids, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISCB3F40.
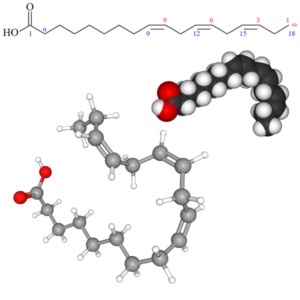
- Oleic Acid (C18H34O2 or C8H17CH=CH(CH2)7COOH)
Oleic Acid: Oleic Acid, Cis-9-Octadecenoic Acid, Cis-Oleic Acid, Elaidoic Acid, Oleate, PubChem CID: 445639, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 112-80-1, ChemIDplus: 112-80-1, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 2UMI9U37CP, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISCC29A0.
- Gamma-Linolenic Acid (C18H30O2)
- Rapeseed Seed Oil (Brassica Napus)Species: Brassica Napus, Family: Brassicaceae, Domain: Plantae, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IHCC0290.
- Omega-9 Acids
- Erucic Acid (C22H42O2)
Erucic Acid: Erucic Acid, Cis-13-Docosenoic Acid, Cis-Erucic Acid, 13-Cis-Docosenoic Acid, 13-Docosenoic Acid, PubChem CID: 5281116, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 112-86-7, ChemIDplus: 112-86-7, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 075441GMF2, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISCC50B0.
- Erucic Acid (C22H42O2)
- Blackcurrant Seed Oil (Ribes Nigrum)Species: Ribes Nigrum, Family: Grossulariaceae, European Medicines Agency: EMA: Ribis Nigri Folium, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IHA42F40.
- Omega-3 Acids
- Eicosapentaenoic Acid
- Docosahexaenoic Acid
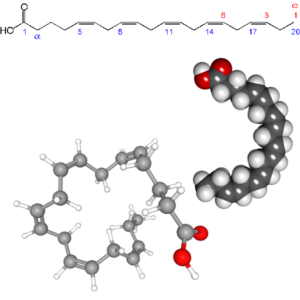
- Alpha-Linolenic Acid (C18H30O2)
 Alpha-Linolenic Acid: Alpha-Linolenic Acid, Linolenic Acid, Linolenate, A-Linolenic Acid, α-Linolenic Acid, ALA,
Alpha-Linolenic Acid: Alpha-Linolenic Acid, Linolenic Acid, Linolenate, A-Linolenic Acid, α-Linolenic Acid, ALA,
PubChem CID: 5280934,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 463-40-1,
ChemIDplus: 463-40-1,
FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 0RBV727H71,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISC3C530,
References:
Cardiovascular Support: MORI, Trevor A. Marine OMEGA-3 Fatty Acids in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Fitoterapia, 2017, 123: 51-58. PMID:28964873,
Immune: GUTIéRREZ, Saray; SVAHN, Sara L.; JOHANSSON, Maria E. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells. International journal of molecular sciences, 2019, 20.20: 5028. PMID:31614433.
- Omega-6 Acids
- Gamma-Linolenic Acid
- Linoleic Acid
- Evening Primrose Oil (EPO) (Oenothera Biennis)Species: Oenothera Biennis, Family: Onagraceae, European Medicines Agency: EMA: Oenotherae Biennis Oleum, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IHA2A8A0, References: Allergy / Immune: GHASEMIAN, Mona; OWLIA, Mohammad Bagher Review of Anti-Inflammatory Herbal Medicines. Advances in pharmacological sciences, 2016, 2016: 9130979. PMID:27247570, MONTSERRAT-DE LA PAZ, S.; et al. Long-chain Fatty Alcohols From Evening Primrose Oil Inhibit the Inflammatory Response in Murine Peritoneal Macrophages. Journal of ethnopharmacology, 2014, 151.1: 131-136. PMID:24239848.
- Omega-6 Acids
- Gamma-Linolenic Acid
- Flax (Linum Usitatissimum)
 Species: Linum Usitatissimum,
Species: Linum Usitatissimum,
Family: Linaceae,
European Medicines Agency: EMA: Lini Semen,
Domain: Plantae,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IHA19730. - Omega-3 Acids
| Supplement Facts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name: | Omega 3-6-9, 1000 mg, 250 Softgels | |
| Serving Size: | 2 Softgels | |
| Servings Per Container: | 125 | |
| Amount Per Serving | %Daily Value | |
| Calories | 20 | |
| Total Fat | 2 g | 3%×) |
| Saturated Fat | <0.5 g | 2%×) |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 1.5 g | † |
| Monounsaturated Fat | <0.5 g | † |
| Flax Seed Oil (Linum Usitatissimum) (Cold-Pressed, Organic) | 1.4 g (1,400 mg) | † |
| Evening Primrose Oil (Oenothera Biennis) (Cold-Presed) (Seed) | 300 mg | † |
| Canola Oil (Brassica Napus) / Omega-9 / Erucic Acid (Cold-Pressed, Non-Gmo) (Seed) | 260 mg | † |
| Black Currant (Ribes Nigrum) (Cold-Presed) (Seed) | 20 mg | † |
| Pumpkin Seed Oil (Cucurbita Pepo) (Cold-Presed) | 20 mg | † |
| ×) Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. † Daily Value not established. |
||
| Manufacturer: | Now Foods |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer Code: | 01837 |
| UPC Code (gtin12): | 733739018373 |
| Package Quantity | |
| Count | 250 |
Other ingredients
Softgel capsule (bovine gelatin, water, glycerin, caramel color, carob powder).
Not manufactured with yeast, wheat, gluten, soy, milk, egg, fish or shellfish ingredients. Produced in a GMP facility that processes other ingredients containing these allergens.
Omega 3-6-9, 1000 mg, 250 Softgels – Suggested Use
Take 2 softgels daily with a meal.
| Recommended Intake | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dose Unit | Dose Value | Frequency | Target Population |
| softgel | 2 | daily | adults |
Warnings
- Caution: For adults only. Consult a physician if taking medication or have a medical condition. Keep out of reach of children.
- Store in a cool, dry place after opening.
- Natural color variation may occur in this product.
Dietary supplements similar to Omega 3-6-9, 1000 mg, 250 Softgels (Now Foods)
The Omega 3-6-9, 1000 mg, 250 Softgels (Now Foods) dietary supplement is available in Belarus and many others countries around the world. In Belarus this supplement contains: ALA, Blackcurrant, Common Evening Primrose, Cucurbita, DHA, EPA, Erucic Acid, Fish Oil, Flax, GLA, Linoleic Acid, Oleic Acid, Omega-3 Acids, Omega-6 Acids, Omega-9 Acids and Rapeseed in its composition.































































Leave a Reply