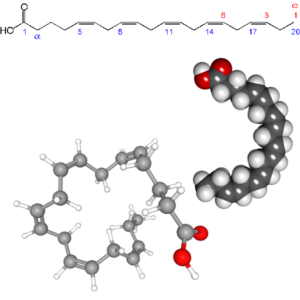
The properties of EPA
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; also icosapentaenoic acid) is an omega-3 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5(n-3). It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid. In chemical structure, EPA is a carboxylic acid with a 20-carbon chain and five cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the third carbon from the omega end.
Sources of Eicosapentaenoic Acid in diet:
- Fatty fish and products made from fatty fish.
- Liver of white fish.
- Seafood and algae.