Calder Philip C.
Nutrients, 2010
Abstract
Long chain fatty acids influence inflammation through a variety of mechanisms; many of these are mediated by, or at least associated with, changes in fatty acid composition of cell membranes. Changes in these compositions can modify membrane fluidity, cell signaling leading to altered gene expression, and the pattern of lipid mediator production. Cell involved in the inflammatory response are typically rich in the n-6 fatty acid arachidonic acid, but the contents of arachidonic acid and of the n-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) can be altered through oral administration of EPA and DHA. Eicosanoids produced from arachidonic acid have roles in inflammation. EPA also gives rise to eicosanoids and these often have differing properties from those of arachidonic acid-derived eicosanoids. EPA and DHA give rise to newly discovered resolvins which are anti-inflammatory and inflammation resolving. Increased membrane content of EPA and DHA (and decreased arachidonic acid content) results in a changed pattern of production of eicosanoids and resolvins. Changing the fatty acid composition of cells involved in the inflammatory response also affects production of peptide mediators of inflammation (adhesion molecules, cytokines etc.). Thus, the fatty acid composition of cells involved in the inflammatory response influences their function; the contents of arachidonic acid, EPA and DHA appear to be especially important. The anti-inflammatory effects of marine n-3 PUFAs suggest that they may be useful as therapeutic agents in disorders with an inflammatory component.
Keywords
cytokine; eicosanoid; fish oil; interleukin; leukocyte; macrophage; monocyte; neutrophil.
Figures
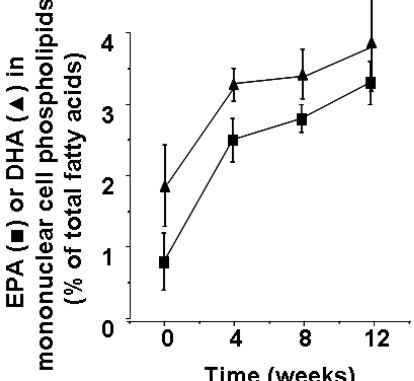
Time course of incorporation of EPA and DHA into human blood mononuclear cells. Healthy subjects supplemented their diet with fish oil capsules providing 2.1 g EPA plus 1.1 g DHA per day for a period of 12 weeks. Blood mononuclear cell phospholipids were isolated at 0, 4, 8 and 12 weeks and their fatty acid composition determined by gas chromatography. Data are mean ± SEM from 8 subjects and are from Yaqoob et al.
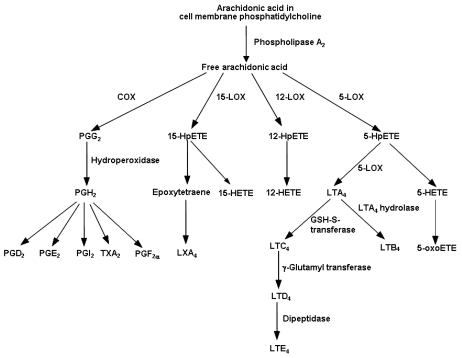
Outline of the pathway of eicosanoid biosynthesis from arachidonic acid. COX, cyclooxygenase; HETE, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; HpETE, hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid; LOX, lipoxygenase; LT, leukotriene; LX, lipoxin; oxoETE, oxoeicosatetraenoic acid; PG, prostaglandin; TX, thromboxane.
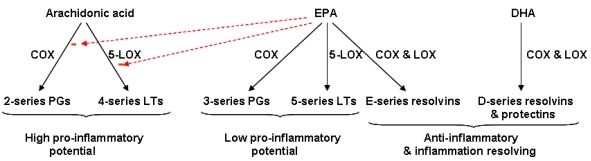
General overview of synthesis and actions of lipid mediators produced from arachidonic acid, EPA and DHA. COX, cyclooxygenase; LOX, lipoxygenase; LT, leukotriene; PG, prostaglandin.
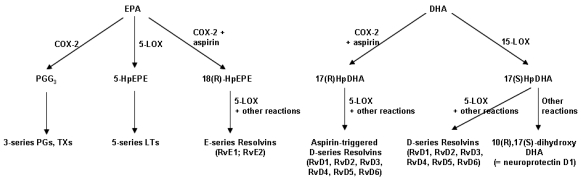
Outline of the pathway of synthesis of resolvins and related mediators from EPA and DHA. COX, cyclooxygenase; HpDHA, hydroperoxydocosahexaenoic acid; HpEPE, hydroperoxyeicosapentaenoic acid; LOX, lipoxygenase; LT, leukotriene; PG, prostaglandin; Rv, resolvin; TX, thromboxane.
| PMID: | 22254027 |
|---|---|
| DOI: | 10.3390/nu2030355 |
| PMCID (Free PMC Article): | PMC3257651 |
| Category: | Immune |
The best supplements with Omega-3 Acids, Docosahexaenoic Acid or Eicosapentaenoic Acid in Immune category:
- Marine Algae Derived Vegan Omega-3, 120 Softgels (Zenwise Health) - M It contains among others: Omega-3 Acids, Docosahexaenoic Acid, Eicosapentaenoic Acid.
- Ashwagandha, 450 mg, 180 Veg Capsules (Now Foods) - Ashwagandha (Withania Somnifera) is an herb that is extensively used in Ayurveda, the traditional herbal system in India. It contains among others: Docosahexaenoic Acid.
- Omega 3-6-9, 1000 mg, 250 Softgels (Now Foods) - Omega 3-6-9 is a blend of Flax-Seed (Linum Usitatissimum), Evening Primrose (Oenothera Biennis), Canola (Brassica Napus) / Omega-9 / Erucic Acid , Black Currant Seed Oils (Ribes Nigrum) - which contains: EPA, DHA, ALA, GLA and Linoleic Acid; and Pumpkin Seed Oils (Cucurbita Pepo). It contains among others: Omega-3 Acids, Docosahexaenoic Acid, Eicosapentaenoic Acid.
- Ashwagandha, 450 mg, 90 Veg Capsules (Now Foods) - Ashwagandha (Whitania somnifera) is an herb that is extensively used in Ayurveda, the traditional herbal system in India. It contains among others: Docosahexaenoic Acid.
Articles similar to "Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes."
- The significance of Eicosapentaenoic Acid for Immune: Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells. (Alterations on the immune system caused by omega-3 fatty acids have been described for 30 years...)
- The role of Eicosapentaenoic Acid in Immune: Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man. (Inappropriate, excessive or uncontrolled inflammation contributes to a range of human diseases...)
- The impact of Eicosapentaenoic Acid on Immune: Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Critical Illness: Anti-Inflammatory, Proresolving, or Both?. (Prognosis and outcomes of critically ill patients are strictly related with inflammatory status...)
- The significance of Eicosapentaenoic Acid for Immune: Long-chain Fatty Acids and Inflammation. (Inflammation plays a key role in many common conditions and diseases...)
- The impact of Eicosapentaenoic Acid on Immune: The Relationship Between the Fatty Acid Composition of Immune Cells and Their Function. (The immune system, including its inflammatory components, is fundamental to host defence against pathogenic invaders...)
Previous article
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man.

























































