Molfino Alessio, et al.
Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2017
Abstract
Prognosis and outcomes of critically ill patients are strictly related with inflammatory status. Inflammation involves a multitude of interactions between different cell types and chemical mediators. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), mainly represented by eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are able to inhibit different pathways including leukocyte chemotaxis, adhesion molecule expression and interactions, and production of inflammatory cytokines, through the action of specialized proresolving mediators (SPMs). SPMs from omega-6 fatty acids, such as lipoxins, and from omega-3 fatty acids such as resolvins, protectins, and maresins, act in reducing/resolving the inflammatory process in critical diseases, stimulating the phases of resolution of inflammation. In this light, the resolution of inflammation is nowadays considered as an active process, instead of a passive process. In critical illness, SPMs regulate the excessive posttrauma inflammatory response, protecting organs from damage. This review focuses on the role of omega-3 PUFAs as pharma nutrition agents in acute inflammatory conditions, highlighting their effects as anti-inflammatory or proresolving agents.
Figures
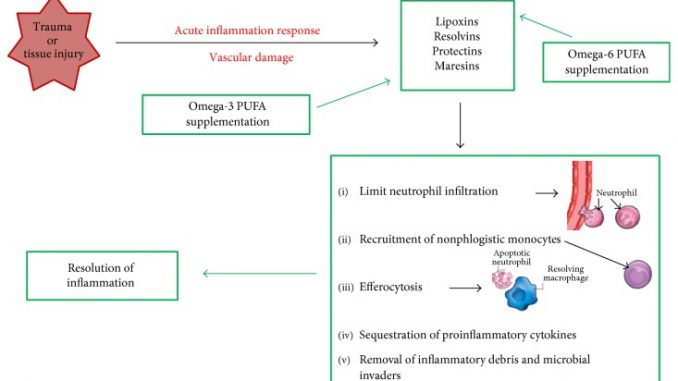
After a trauma or tissue injury, there is a vascular damage inducing the acute inflammatory response. The specialized lipid mediators (SPMs), derived from omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acid storage, act as proresolving mediators. The SPM class which initiates to resolve inflammation is represented by lipoxins that are able to limit neutrophil infiltration. Lipoxins and resolvins stimulate the recruitment of nonphlogistic monocytes. Resolvins and protectins stimulate the resolving macrophages to clear apoptotic neutrophils in the efferocytosis process. Signs of resolution include sequestration of proinflammatory cytokines and removal of inflammatory debris and microbial invaders. Maresins stimulate reepithelialization, wound healing, and tissue regeneration. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation may enhance proresolving inflammatory responses via their capacity to regulate the expression of proinflammatory cytokines through the production of SPMs. PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids.
| PMID: | 28694914 |
|---|---|
| DOI: | 10.1155/2017/5987082 |
| PMCID (Free PMC Article): | PMC5488236 |
| Category: | Immune |
The best supplements with Omega-3 Acids, Docosahexaenoic Acid or Eicosapentaenoic Acid in Immune category:
- Marine Algae Derived Vegan Omega-3, 120 Softgels (Zenwise Health) - M It contains among others: Omega-3 Acids, Docosahexaenoic Acid, Eicosapentaenoic Acid.
- Ashwagandha, 450 mg, 180 Veg Capsules (Now Foods) - Ashwagandha (Withania Somnifera) is an herb that is extensively used in Ayurveda, the traditional herbal system in India. It contains among others: Docosahexaenoic Acid.
- Omega 3-6-9, 1000 mg, 250 Softgels (Now Foods) - Omega 3-6-9 is a blend of Flax-Seed (Linum Usitatissimum), Evening Primrose (Oenothera Biennis), Canola (Brassica Napus) / Omega-9 / Erucic Acid , Black Currant Seed Oils (Ribes Nigrum) - which contains: EPA, DHA, ALA, GLA and Linoleic Acid; and Pumpkin Seed Oils (Cucurbita Pepo). It contains among others: Omega-3 Acids, Docosahexaenoic Acid, Eicosapentaenoic Acid.
- Ashwagandha, 450 mg, 90 Veg Capsules (Now Foods) - Ashwagandha (Whitania somnifera) is an herb that is extensively used in Ayurveda, the traditional herbal system in India. It contains among others: Docosahexaenoic Acid.
Articles similar to "Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Critical Illness: Anti-Inflammatory, Proresolving, or Both?."
- The significance of Eicosapentaenoic Acid for Immune: Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Immune Cells. (Alterations on the immune system caused by omega-3 fatty acids have been described for 30 years...)
- The role of Eicosapentaenoic Acid in Immune: Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man. (Inappropriate, excessive or uncontrolled inflammation contributes to a range of human diseases...)
- The significance of Eicosapentaenoic Acid for Immune: Long-chain Fatty Acids and Inflammation. (Inflammation plays a key role in many common conditions and diseases...)
- The role of Eicosapentaenoic Acid in Immune: Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes. (Long chain fatty acids influence inflammation through a variety of mechanisms; many of these are mediated by, or at least associated with, changes in fatty acid composition of cell membranes...)
- The impact of Eicosapentaenoic Acid on Immune: The Relationship Between the Fatty Acid Composition of Immune Cells and Their Function. (The immune system, including its inflammatory components, is fundamental to host defence against pathogenic invaders...)
Previous article
The Relationship Between the Fatty Acid Composition of Immune Cells and Their Function.
Next article
The Role for Dietary omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation in Older Adults.

























































