Molfino Alessio, et al.
Nutrients, 2014
Abstract
Optimal nutrition is one of the most important determinants of healthier ageing, reducing the risk of disability, maintaining mental and physical functions, and thus preserving and ensuring a better quality of life. Dietary intake and nutrient absorption decline with age, thus increasing the risk of malnutrition, morbidity and mortality. Specific nutrients, particularly long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), might have the potential of preventing and reducing co-morbidities in older adults. Omega-3 PUFAs are able to modulate inflammation, hyperlipidemia, platelet aggregation, and hypertension. Different mechanisms contribute to these effects, including conditioning cell membrane function and composition, eicosanoid production, and gene expression. The present review analyzes the influence of omega-3 PUFAs status and intake on brain function, cardiovascular system, immune function, muscle performance and bone health in older adults. Omega-3 FAs may have substantial benefits in reducing the risk of cognitive decline in older people. The available data encourage higher intakes of omega-3 PUFAs in the diet or via specific supplements. More studies are needed to confirm the role of omega-3 FAs in maintaining bone health and preventing the loss of muscle mass and function associated with ageing. In summary, omega-3 PUFAs are now identified as potential key nutrients, safe and effective in the treatment and prevention of several negative consequences of ageing.
Figures
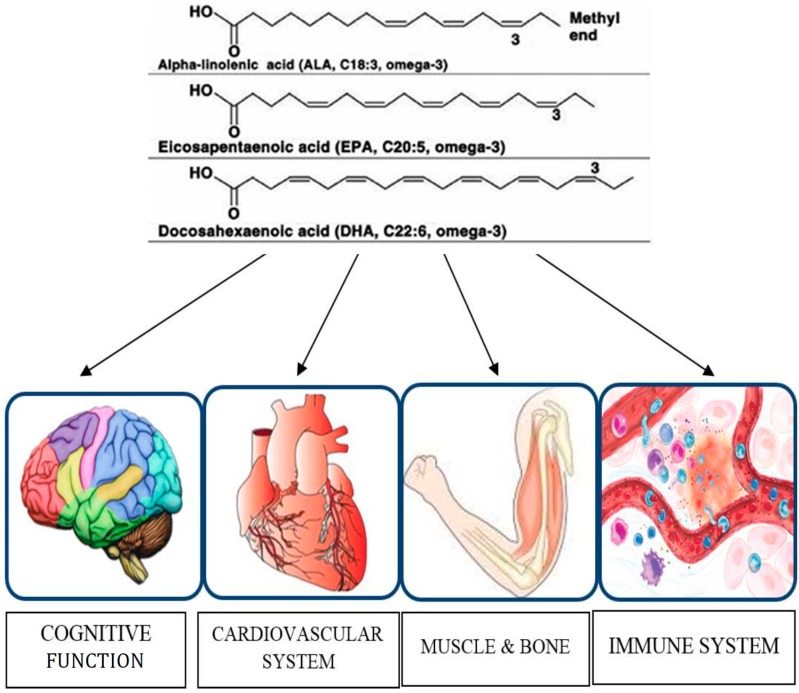
Organs and functions modulated by omega-3 PUFAs in older adults.
| PMID: | 25285409 |
|---|---|
| DOI: | 10.3390/nu6104058 |
| PMCID (Free PMC Article): | PMC4210907 |
| Category: | General properties of Omega-3 Acids |
Articles similar to "The Role for Dietary omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation in Older Adults."
- The properties of Omega-3 Acids: A Comprehensive Review of Chemistry, Sources and Bioavailability of Omega-3 Fatty Acids. (Omega-3 fatty acids, one of the key building blocks of cell membranes, have been of particular interest to scientists for many years...)
- The properties of Omega-3 Acids: Marine omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: Effects, Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance. (Inflammation is a condition which contributes to a range of human diseases...)
- The properties of Omega-3 Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, hepatic lipid metabolism, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. (Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids belong to a family of polyunsaturated fatty acids that are known to have important beneficial effects on metabolism and inflammation...)
- The properties of Omega-3 Acids: Omega 3 Fatty Acids in the Elderly. (Population ageing affects the entire world population...)
Previous article
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Critical Illness: Anti-Inflammatory, Proresolving, or Both?.

























































