Maywald Martina, Wessels Inga, Rink Lothar
International journal of molecular sciences, 2017
Abstract
Zinc homeostasis is crucial for an adequate function of the immune system. Zinc deficiency as well as zinc excess result in severe disturbances in immune cell numbers and activities, which can result in increased susceptibility to infections and development of especially inflammatory diseases. This review focuses on the role of zinc in regulating intracellular signaling pathways in innate as well as adaptive immune cells. Main underlying molecular mechanisms and targets affected by altered zinc homeostasis, including kinases, caspases, phosphatases, and phosphodiesterases, will be highlighted in this article. In addition, the interplay of zinc homeostasis and the redox metabolism in affecting intracellular signaling will be emphasized. Key signaling pathways will be described in detail for the different cell types of the immune system. In this, effects of fast zinc flux, taking place within a few seconds to minutes will be distinguish from slower types of zinc signals, also designated as "zinc waves", and late homeostatic zinc signals regarding prolonged changes in intracellular zinc.
Keywords
homeostatic zinc signal; immune function; innate and adaptive immunity; signaling pathways; zinc deficiency; zinc flux; zinc wave.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.Figures
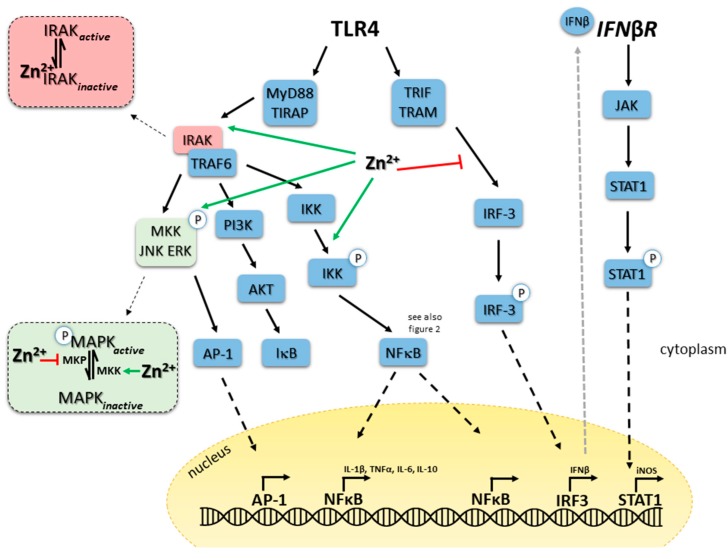 Zinc in TLR4 triggered signaling, illustrating explanations in the text. Black arrow: activation, green arrow: activating function of zinc, red T bar: inhibiting function of zinc, black dotted arrow, translocation of the molecule to nucleus, grey dotted arrow: secretion of the molecule. Abbreviations : ERK: extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase; IFN: interferon; IRAK: Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; IκB: Inhibitor of NFκB; IKK: IκB kinase; IRF: interferon related factor; JAK: JNK janus kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal Kinase; MAPK: mitogen activated protein kinases MEK: MAPK/Erk kinase; MKK: MAPK kinase; MKP: MAPK phosphatase; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; NFκB: nuclear factor (NF) κB. PI3K: phosphatidyl-inositol-3-phosphate; STAT: signal transducers and activators of transcription; TBK: Tank-binding kinase 1; TIRAP: toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain containing adaptor protein; TLR: toll like receptor; TRAF: TNF receptor-associated factor; TRAM: TRIF-related adaptor molecule; TRIF: Toll-interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing adaptor-inducing interferon.
Zinc in TLR4 triggered signaling, illustrating explanations in the text. Black arrow: activation, green arrow: activating function of zinc, red T bar: inhibiting function of zinc, black dotted arrow, translocation of the molecule to nucleus, grey dotted arrow: secretion of the molecule. Abbreviations : ERK: extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase; IFN: interferon; IRAK: Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; IκB: Inhibitor of NFκB; IKK: IκB kinase; IRF: interferon related factor; JAK: JNK janus kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal Kinase; MAPK: mitogen activated protein kinases MEK: MAPK/Erk kinase; MKK: MAPK kinase; MKP: MAPK phosphatase; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; NFκB: nuclear factor (NF) κB. PI3K: phosphatidyl-inositol-3-phosphate; STAT: signal transducers and activators of transcription; TBK: Tank-binding kinase 1; TIRAP: toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain containing adaptor protein; TLR: toll like receptor; TRAF: TNF receptor-associated factor; TRAM: TRIF-related adaptor molecule; TRIF: Toll-interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing adaptor-inducing interferon.
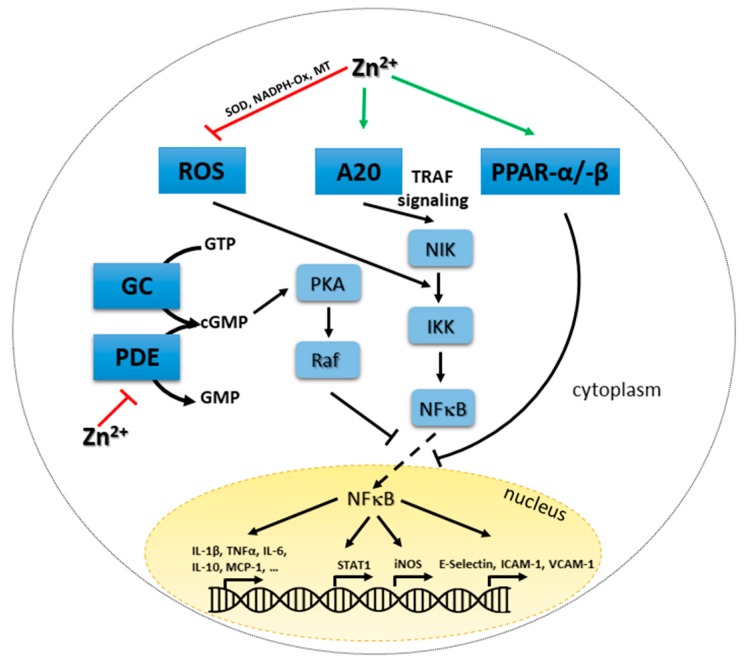 Complex impact of zinc on NFκB-centered signaling as illustration of signaling pathways described in the text. Red T bar: inhibitory function of zinc, green arrow: activating function of zinc, black T bar: inhibition, black arrow activation. Abbreviations : cGMP: cyclic guanine monophosphate; GC: guanine cyclase; GMP: guanine monophosphate; GTP: guanine triphosphate; ICAM: intercellular adhesion molecule; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; IKK: IκB kinase; IL: interleukin; MCP: monocyte chemoattractant protein; NIK: NFκB-inducing kinase; NFκB: nuclear factor (NF)κB; PDE: phosphodiesterase; PKA: protein kinase A; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; ROS: reactive oxygen species; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; VCAM: vascular cell adhesion molecule.
Complex impact of zinc on NFκB-centered signaling as illustration of signaling pathways described in the text. Red T bar: inhibitory function of zinc, green arrow: activating function of zinc, black T bar: inhibition, black arrow activation. Abbreviations : cGMP: cyclic guanine monophosphate; GC: guanine cyclase; GMP: guanine monophosphate; GTP: guanine triphosphate; ICAM: intercellular adhesion molecule; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; IKK: IκB kinase; IL: interleukin; MCP: monocyte chemoattractant protein; NIK: NFκB-inducing kinase; NFκB: nuclear factor (NF)κB; PDE: phosphodiesterase; PKA: protein kinase A; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; ROS: reactive oxygen species; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; VCAM: vascular cell adhesion molecule.
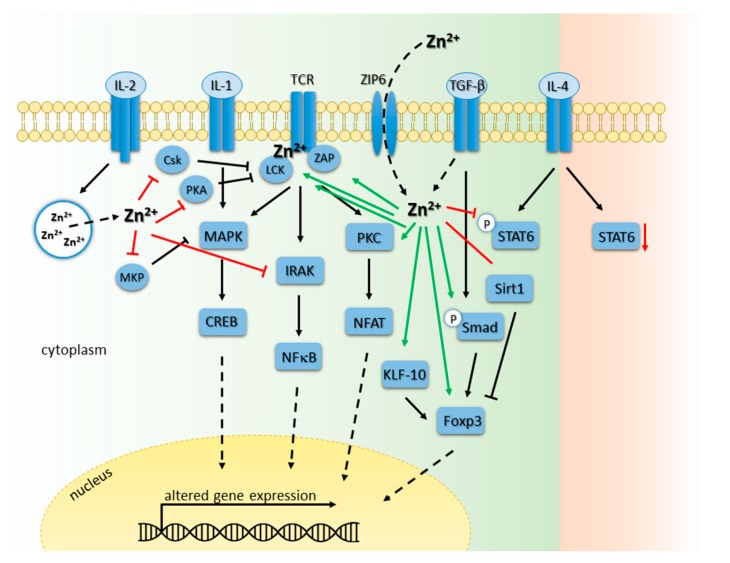 Influence of zinc signals on T cell signaling pathways. This figure presents an overview of T cell receptor (TCR)-, Interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R)-, IL-2R-, IL-4R-, Transforming growth factor β1 receptor (TGF-β1R)-signaling in T cells, as well as zinc flux via zinc transporter ZIP6. Signaling pathways are described in detail in the text. Black arrow: activation, green arrow: activating function of zinc, red T bar: inhibiting function of zinc, black dotted arrow, translocation of the molecule to nucleus. Abbreviations : CREB: cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein; Csk: c-src tyrosine kinase; Foxp3: forkhead-box-protein P3; IL: Interleukin; IRAK: interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; KLF-10: krüppel-like factor-10; Lck: lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MKP: MAP-kinase phosphatase; NFAT: nuclear factor of activated T cells; NFκB: nuclear factor kappa B; PKA: protein kinase A; PKC: protein kinase C; SIRT1: Sirtuin1; STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription; TCR: T cell receptor; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor β1. ZAP: zeta-chain (TCR)-associated protein kinase.
Influence of zinc signals on T cell signaling pathways. This figure presents an overview of T cell receptor (TCR)-, Interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R)-, IL-2R-, IL-4R-, Transforming growth factor β1 receptor (TGF-β1R)-signaling in T cells, as well as zinc flux via zinc transporter ZIP6. Signaling pathways are described in detail in the text. Black arrow: activation, green arrow: activating function of zinc, red T bar: inhibiting function of zinc, black dotted arrow, translocation of the molecule to nucleus. Abbreviations : CREB: cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein; Csk: c-src tyrosine kinase; Foxp3: forkhead-box-protein P3; IL: Interleukin; IRAK: interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase; KLF-10: krüppel-like factor-10; Lck: lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MKP: MAP-kinase phosphatase; NFAT: nuclear factor of activated T cells; NFκB: nuclear factor kappa B; PKA: protein kinase A; PKC: protein kinase C; SIRT1: Sirtuin1; STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription; TCR: T cell receptor; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor β1. ZAP: zeta-chain (TCR)-associated protein kinase.| PMID: | 29064429 |
|---|---|
| PMCID (Free PMC Article): | PMC5666901 |
| DOI: | 10.3390/ijms18102222 |
| Category: | Immune |
The best supplements with Zinc in Immune category:
- Zinc Picolinate, 100 Tablets (Solgar) - Zinc promotes healthy skin and supports normal taste and vision. It contains among others: Zinc.
- Immune Defence - Zinc Lozenges with Rosehip and Acerola - Your immune system needs daily support to stay in good form, to be able to fight off any pathogens trying to enter your system and to witstand the impact of stress on your body and mind. It contains among others: Zinc.
- L-OptiZinc, 30 mg, 100 Veg Capsules (Now Foods) - L-OptiZinc is a form of Zinc complexed with the amino acids Methionine. It contains among others: Zinc.
- Zinc, 50 mg, 250 Tablets (Now Foods) - Zinc is essential to the normal function of many organs and systems within the body including the skeletal, immune, neurological, and endocrine systems. It contains among others: Zinc.
- Zinc Picolinate, 50 mg, 120 Veg Capsules (Now Foods) - Zinc is essential to the normal function of many organs and systems within the body including the skeletal, immune, neurological, and endocrine systems. It contains among others: Zinc.
Articles similar to "Zinc Signals and Immunity."
- The significance of Zinc for Immune: Zinc as a Gatekeeper of Immune Function. (After the discovery of zinc deficiency in the 1960s, it soon became clear that zinc is essential for the function of the immune system...)
- The impact of Zinc on Immune: Roles of Zinc Signaling in the Immune System. (Zinc (Zn) is an essential micronutrient for basic cell activities such as cell growth, differentiation, and survival...)
- The significance of Zinc for Immune: Zinc and Immunity: An Essential Interrelation. (The significance of the essential trace element zinc for immune function has been known for several decades...)
- The role of Zinc in Immune: Zinc, Aging, and Immunosenescence: An Overview. (Zinc plays an essential role in many biochemical pathways and participates in several cell functions, including the immune response...)
- The impact of Zinc on Immune: Zinc Signals and Immune Function. (For more than 50 years, it has been known that zinc deficiency compromises immune function...)
- The significance of Zinc for Immune: Zinc: Dietary Intake and Impact of Supplementation on Immune Function in Elderly. (The diet in the elderly does not provide a sufficient level of nutrients needed to maintain an adequate healthy status leading to micronutrient deficiencies and impaired immune response with subsequent development of degenerative diseases...)
- The role of Zinc in Immune: Zinc in Innate and Adaptive Tumor Immunity. (Zinc is important...)
- The impact of Zinc on Immune: Zinc in Human Health: Effect of Zinc on Immune Cells. (Although the essentiality of zinc for plants and animals has been known for many decades, the essentiality of zinc for humans was recognized only 40 years ago in the Middle East...)
- The significance of Zinc for Immune: Immune-enhancing Role of Vitamin C and Zinc and Effect on Clinical Conditions. (Vitamin C concentrations in the plasma and leukocytes rapidly decline during infections and stress...)
- The role of Zinc in Immune: Zinc: Role in Immunity, Oxidative Stress and Chronic Inflammation. (Purpose of review: Zinc is essential for multiple cellular functions including immunity...)
Previous article
Zinc as a Gatekeeper of Immune Function.

























































