John Erica, et al.
Journal of translational medicine, 2010
Abstract
Zinc is important. It is the second most abundant trace metal with 2-4 grams in humans. It is an essential trace element, critical for cell growth, development and differentiation, DNA synthesis, RNA transcription, cell division, and cell activation. Zinc deficiency has adverse consequences during embryogenesis and early childhood development, particularly on immune functioning. It is essential in members of all enzyme classes, including over 300 signaling molecules and transcription factors. Free zinc in immune and tumor cells is regulated by 14 distinct zinc importers (ZIP) and transporters (ZNT1-8). Zinc depletion induces cell death via apoptosis (or necrosis if apoptotic pathways are blocked) while sufficient zinc levels allows maintenance of autophagy. Cancer cells have upregulated zinc importers, and frequently increased zinc levels, which allow them to survive. Based on this novel synthesis, approaches which locally regulate zinc levels to promote survival of immune cells and/or induce tumor apoptosis are in order.
Figures
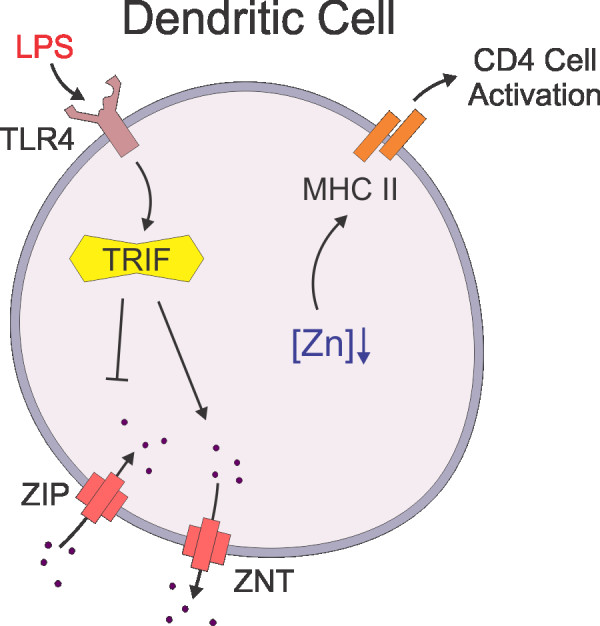 Intracellular Zinc Levels Fall During Dendritic Cell Maturation. After the detection of LPS (Pathogen Associated PAMPs) by TLR4 and activation of TRIF, zinc importers (ZIPs) expression is diminished while transporters (ZNTs) expression is increased. The resulting decrease in intracellular zinc concentration promotes the surface expression of MHC-II and thus the maturation of DCs.
Intracellular Zinc Levels Fall During Dendritic Cell Maturation. After the detection of LPS (Pathogen Associated PAMPs) by TLR4 and activation of TRIF, zinc importers (ZIPs) expression is diminished while transporters (ZNTs) expression is increased. The resulting decrease in intracellular zinc concentration promotes the surface expression of MHC-II and thus the maturation of DCs.
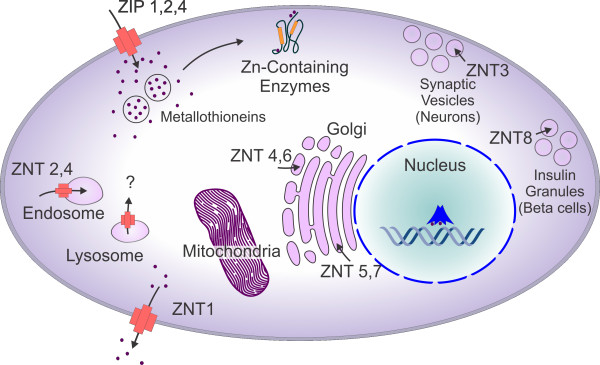 Localization and transport of zinc in a mammalian cell. Cellular localization and function of ZIP and ZNT zinc transporter family members. Arrows indicate the direction of zinc mobilization. ZIP1, 2 and 4 are induced in zinc deficient conditions, while ZNT-1 and 2 members are induced by zinc administration. In general zinc efflux is associated with enhanced susceptibility to apoptosis and higher levels with protection/autophagy.
Localization and transport of zinc in a mammalian cell. Cellular localization and function of ZIP and ZNT zinc transporter family members. Arrows indicate the direction of zinc mobilization. ZIP1, 2 and 4 are induced in zinc deficient conditions, while ZNT-1 and 2 members are induced by zinc administration. In general zinc efflux is associated with enhanced susceptibility to apoptosis and higher levels with protection/autophagy.| PMID: | 21087493 |
|---|---|
| PMCID (Free PMC Article): | PMC3002329 |
| DOI: | 10.1186/1479-5876-8-118 |
| Category: | Immune |
The best supplements with Zinc in Immune category:
- Zinc Picolinate, 100 Tablets (Solgar) - Zinc promotes healthy skin and supports normal taste and vision. It contains among others: Zinc.
- Immune Defence - Zinc Lozenges with Rosehip and Acerola - Your immune system needs daily support to stay in good form, to be able to fight off any pathogens trying to enter your system and to witstand the impact of stress on your body and mind. It contains among others: Zinc.
- L-OptiZinc, 30 mg, 100 Veg Capsules (Now Foods) - L-OptiZinc is a form of Zinc complexed with the amino acids Methionine. It contains among others: Zinc.
- Zinc, 50 mg, 250 Tablets (Now Foods) - Zinc is essential to the normal function of many organs and systems within the body including the skeletal, immune, neurological, and endocrine systems. It contains among others: Zinc.
- Zinc Picolinate, 50 mg, 120 Veg Capsules (Now Foods) - Zinc is essential to the normal function of many organs and systems within the body including the skeletal, immune, neurological, and endocrine systems. It contains among others: Zinc.
Articles similar to "Zinc in Innate and Adaptive Tumor Immunity."
- The significance of Zinc for Immune: Zinc as a Gatekeeper of Immune Function. (After the discovery of zinc deficiency in the 1960s, it soon became clear that zinc is essential for the function of the immune system...)
- The role of Zinc in Immune: Zinc Signals and Immunity. (Zinc homeostasis is crucial for an adequate function of the immune system...)
- The impact of Zinc on Immune: Roles of Zinc Signaling in the Immune System. (Zinc (Zn) is an essential micronutrient for basic cell activities such as cell growth, differentiation, and survival...)
- The significance of Zinc for Immune: Zinc and Immunity: An Essential Interrelation. (The significance of the essential trace element zinc for immune function has been known for several decades...)
- The role of Zinc in Immune: Zinc, Aging, and Immunosenescence: An Overview. (Zinc plays an essential role in many biochemical pathways and participates in several cell functions, including the immune response...)
- The impact of Zinc on Immune: Zinc Signals and Immune Function. (For more than 50 years, it has been known that zinc deficiency compromises immune function...)
- The significance of Zinc for Immune: Zinc: Dietary Intake and Impact of Supplementation on Immune Function in Elderly. (The diet in the elderly does not provide a sufficient level of nutrients needed to maintain an adequate healthy status leading to micronutrient deficiencies and impaired immune response with subsequent development of degenerative diseases...)
- The impact of Zinc on Immune: Zinc in Human Health: Effect of Zinc on Immune Cells. (Although the essentiality of zinc for plants and animals has been known for many decades, the essentiality of zinc for humans was recognized only 40 years ago in the Middle East...)
- The significance of Zinc for Immune: Immune-enhancing Role of Vitamin C and Zinc and Effect on Clinical Conditions. (Vitamin C concentrations in the plasma and leukocytes rapidly decline during infections and stress...)
- The role of Zinc in Immune: Zinc: Role in Immunity, Oxidative Stress and Chronic Inflammation. (Purpose of review: Zinc is essential for multiple cellular functions including immunity...)
Previous article
Zinc and Immunity: An Essential Interrelation.

























































