

Astaksantyna marki NOW® pochodzi z niemodyfikowanych genetycznie mikroalg Haematococcus pluvialis, które zawierają naturalną luteinę, kantaksantynę oraz beta-karoten. Jest to produkt o ekstra mocy i ma ponad dwukrotnie większą zawartość astaksantyny (10 mg W Kapsułce) niż nasz produkt o standardowej mocy (4 mg W Kapsułce).
- non-GMO
- Made w/o Gluten
- Dairy Free
- Egg Free
- Kosher
Astaxanthin, 10 mg, 60 Softgels (Now Foods) – Składniki
- Haematococcus Pluvialis (Haematococcus Pluvialis)Species: Haematococcus Pluvialis, Family: Haematococcaceae, Domain: Eukaryota, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IHD09670.
- Astaksantyna (C40H52O4)
Astaksantyna jest jednym z najsilniejszych karotenoidów przeciwutleniających w swojej klasie, ze względu na jej wyjątkową zdolność do przekraczania bariery krew-mózg / oko. W badaniach klinicznych wykazano, że pomaga wzmocnić naturalną zdolność oka do skupiania się na bliskich obiektach.
Astaksantyna: Astaxanthin, Astaxanthine, Ovoester, PubChem CID: 5281224, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 472-61-7, ChemIDplus: 472-61-7, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 8XPW32PR7I, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISB2D540, References: Immune: HUSSEIN, Ghazi; et al. Astaxanthin, a Carotenoid With Potential in Human Health and Nutrition. Journal of natural products, 2006, 69.3: 443-449. PMID:16562856, CHEW, Boon P.; PARK, Jean Soon Carotenoid Action on the Immune Response. The Journal of nutrition, 2004, 134.1: 257S-261S. PMID:14704330, Antioxidants: HIGUERA-CIAPARA, I.; FéLIX-VALENZUELA, L.; GOYCOOLEA, F. M. Astaxanthin: A Review of Its Chemistry and Applications. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 2006, 46.2: 185-196. PMID:16431409, Eye Health: GIANNACCARE, Giuseppe; et al. Clinical Applications of Astaxanthin in the Treatment of Ocular Diseases: Emerging Insights. Marine drugs, 2020, 18.5: 239. PMID:32370045, LI, Hui; et al. The effect of astaxanthin on inflammation in hyperosmolarity of experimental dry eye model in vitro and in vivo. Experimental Eye Research, 2020, 197: 108113. PMID:32531188, Cardiovascular Support: FASSETT, Robert G.; COOMBES, Jeff S. Astaxanthin, oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular disease. Future cardiology, 2009, 5.4: 333-342. PMID:19656058, FASSETT, Robert G.; COOMBES, Jeff S. Astaxanthin: a potential therapeutic agent in cardiovascular disease. Marine drugs, 2011, 9.3: 447-465. PMID:21556169.
- Canthaxanthin (C40H52O2)
Canthaxanthin: Canthaxanthin, Orobronze, Carophyll Red, Beta,Beta-Carotene-4,4′-Dione, PubChem CID: 5281227, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 514-78-3, ChemIDplus: 514-78-3, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 4C3C6403MU, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISD0BD80, References: Immune: CHEW, Boon P.; PARK, Jean Soon Carotenoid Action on the Immune Response. The Journal of nutrition, 2004, 134.1: 257S-261S. PMID:14704330, Eye Health: JOHRA, Fatima Tuj; et al. A Mechanistic Review of β-Carotene, Lutein, and Zeaxanthin in Eye Health and Disease. Antioxidants, 2020, 9.11: 1046. PMID:33114699.
- Witamina A (β-Karoten) (C40H56)
Witamina A (β-Karoten): Beta-Carotene, Beta Carotene, Provitamin A, Betacarotene, Solatene, Carotaben, Provatene, Serlabo, PubChem CID: 5280489, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 7235-40-7, ChemIDplus: 7235-40-7, WHO Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System: ATC code: A11CA02, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: 01YAE03M7J, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2AB980-1.
- Luteina (C40H56O2)
Luteina: Lutein, Luteine, Xanthophyll, Lutamax, PubChem CID: 5281243, Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 127-40-2, ChemIDplus: 127-40-2, FDA Substance Registration System – Unique Ingredient Identifier: UNII: X72A60C9MT, The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: ISAEB690, References: Immune: CHEW, Boon P.; PARK, Jean Soon Carotenoid Action on the Immune Response. The Journal of nutrition, 2004, 134.1: 257S-261S. PMID:14704330, Eye Health: WANG, Xin; et al. Role of lutein supplementation in the management of age-related macular degeneration: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ophthalmic research, 2014, 52.4: 198-205. PMID:25358528, MA, Le; et al. Lutein and zeaxanthin intake and the risk of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. British Journal of Nutrition, 2012, 107.3: 350-359. PMID:21899805. - Canthaxanthin (C40H52O2)
- Astaksantyna (C40H52O4)
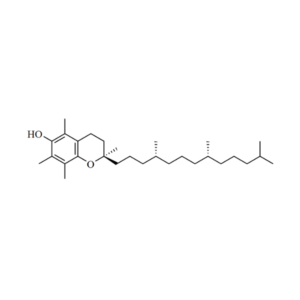
- Witamina E (α-Tokoferol) (C29H50O2)
Klinicznie wykazano, że tokoferole z witaminy E zmniejszają stres oksydacyjny, jednocześnie chroniąc integralność dodatkowych karotenoidów, pomagając zmniejszyć częstość występowania typowych problemów związanych z wiekiem wpływających na wzrok. Witamina E jest silnym przeciwutleniaczem i ma zdolność modulowania funkcji odpornościowych. Jest ważnym składnikiem odżywczym dla utrzymania układu odpornościowego, szczególnie u osób starszych. Spożycie powyżej obecnie zalecanego poziomu witaminy E może poprawić odpowiedź immunologiczną i zapalną i może być związane ze zmniejszonym ryzykiem chorób zakaźnych. Witamina E (α-Tokoferol): Vitamin E, Alpha-Tocopherol, Α-Tocopherol, D-Alpha-Tocopherol, DL-Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate, DL-Alpha-Tocopheryl Acetate,
Witamina E (α-Tokoferol): Vitamin E, Alpha-Tocopherol, Α-Tocopherol, D-Alpha-Tocopherol, DL-Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate, DL-Alpha-Tocopheryl Acetate,
PubChem CID: 14985,
Chemical Abstracts Service: CAS: 59-02-9,
ChemIDplus: 59-02-9,
The Best Supplements – Unique Ingredient Identifier: TBSI ID: IS2A4450,
References:
Immune: LEE, Ga Young; et al. The Role of Vitamin E in Immunity. Nutrients, 2018, 10.11: 1614. PMID:30388871, MEYDANI, Simin Nikbin; LEWIS, Erin Diane; WU, Dayong Perspective: Should Vitamin E Recommendations for Older Adults Be Increased?. Advances in Nutrition, 2018, 9.5: 533-543. PMID:30107519,
Eye Health: FERNáNDEZ-ARAQUE, Ana; et al. The antioxidants in the process of ocular pathology. Nutrición Hospitalaria, 2017, 34.2: 469-478. PMID:28421807, SINDACO, Daniele; et al. Ophthalmologic evaluation in vitamin-E deficiency: A case report. European Journal of Ophthalmology, 2020, 2020: 1120672120970112. PMID:33143445.
| Supplement Facts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name: | Astaxanthin, 10 mg, 60 Softgels | |
| Serving Size: | 1 Softgel | |
| Amount Per Serving | % Daily Value | |
| Calories | 5 | |
| Natural Astaxanthin (Haematococcus Pluvialis) Extract | 10 mg | † |
| † Daily Value not established. | ||
| Manufacturer: | Now Foods |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer Code: | 02251 |
| UPC Code (gtin12): | 733739022516 |
| Package Quantity | |
| Count | 60 |
Pozostałe składniki
Olej z krokosza barwierskiego, kapsułka żelowa (Żelatyna, Woda, Gliceryna) oraz witamina E (W Postaci Naturalnego D-Alfa-Tokoferolu). Witamina E z soi.
W procesie produkcji nie wykorzystano składników pochodzących z pszenicy, glutenu, mleka, jajek, ryb, skorupiaków ani orzechów drzewnych. Wyprodukowano w zakładzie stosującym zasady dobrej praktyki wytwarzania (GMP), w którym przetwarza się składniki innych preparatów zawierające te alergeny.
Dawkowanie suplementu – Astaxanthin Extra Strength 10 mg – Ochrona komórek* – 60 kapsułek żelowych
Przyjmować 1 kapsułkę dziennie, przy posiłku zawierającym tłuszcz.
| Recommended Intake | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dose Unit | Dose Value | Frequency | Target Population |
| softgel | 1 | daily | adults |
Uwaga
- Produkt przeznaczony do stosowania wyłącznie przez osoby dorosłe. Kobiety ciężarne, karmiące oraz osoby przyjmujące leki lub mające schorzenia powinny skonsultować się z lekarzem.
- Po otwarciu przechowywać w miejscu chłodnym i suchym. Przechowywać w miejscu niedostępnym dla dzieci.
- Pamiętaj o recyklingu.
Suplementy diety podobne do Astaxanthin, 10 mg, 60 Softgels (Now Foods)
Suplement diety Astaxanthin, 10 mg, 60 Softgels (Now Foods) jest dostępny w Polsce i wielu innych krajach na całym świecie. W Polsce ten suplement zawiera w swoim składzie następujące składniki: Astaxanthin, Canthaxanthin, Haematococcus Pluvialis, Lutein, Vitamin A and Vitamin E.




























































Leave a Reply