Meydani Simin Nikbin, Lewis Erin Diane, Wu Dayong
Advances in Nutrition, 2018
Abstract
Current vitamin E requirements are uniformly applied across the population for those >14 y of age. However, aging is associated with alterations in cellular and physiologic functions, which are affected by vitamin E. Therefore, it is questionable whether vitamin E requirements can be uniformly applied to all adult age categories. With aging, there is dysregulation of the immune system in which there are decreased cell-mediated and pathogen defense responses coupled with an overactive, prolonged inflammatory state. Both animal and human studies in the aged suggest that intake above currently recommended levels of vitamin E may improve immune and inflammatory responses and be associated with a reduced risk of infectious disease. We review the evidence that was considered in establishing the current requirements for vitamin E and highlight data that should be considered in determining the vitamin E requirements in older adults, particularly focusing on the evidence suggesting a benefit of increased vitamin E intake on immune function and inflammatory processes and resistance to infection. The main objective of this Perspective is to initiate the discussion of whether the current Dietary Reference Intake for vitamin E should be increased for the older population. We make this suggestion on the basis of mechanistic studies showing biological plausibility, correction of a major cellular dysfunction in older adults, and strong evidence from several animal and a few human studies indicating a reduction in risk and morbidity from infections.
Figures
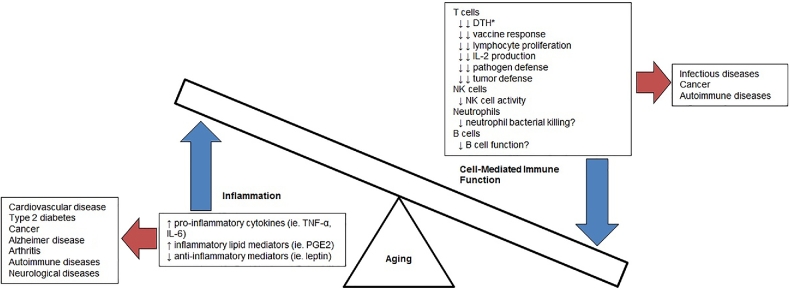
Dysregulation of inflammation and cell-mediated immune function that occurs with aging and the relation to the pathogenesis of various age-associated diseases. Number of arrows indicate the strength of evidence, with double arrows indicating strong evidence and single arrow indicating moderate evidence. *Indicates skin response that is an in vivo measure of cell-mediated immune function and assessment of cell-mediated immune function. DTH, delayed-type hypersensitivity; PGE2, prostaglandin E2.
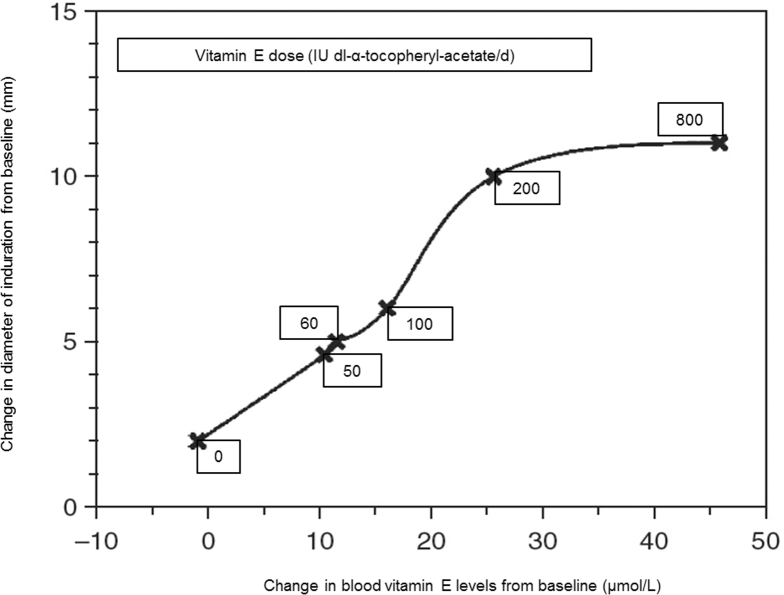
Relation between changes in delayed-type hypersensitivity skin response (diameter of induration) and changes in blood vitamin E concentrations from baseline after 30 d of supplementation with different doses of vitamin E in healthy older adults. Reproduced from reference with permission.
| PMID: | 30107519 |
|---|---|
| DOI: | 10.1093/advances/nmy035 |
| PMCID (Free PMC Article): | PMC6140432 |
| Category: | Immune |
The best supplements with Vitamin E in Immune category:
- Immunity 911 - Extra Powerful Ingredients for Your Stronger Immunity -
Immunity 911 - Advanced Immune Boster Formula Your First Line Of Defense Against Infection!
Viruses are floating all around us, ready to filter into our body any moment completely unnoticed. It contains among others: Vitamin E. - Immune Defence - Zinc Lozenges with Rosehip and Acerola - Your immune system needs daily support to stay in good form, to be able to fight off any pathogens trying to enter your system and to witstand the impact of stress on your body and mind. It contains among others: Vitamin E.
- Astaxanthin, 10 mg, 60 Softgels (Now Foods) - NOW Astaxanthin is a naturally occurring carotenoid that, due to its unique structure, performs an important role in cellular free radical protection and healthy immune system responses. It contains among others: Vitamin E.
Articles similar to "Perspective: Should Vitamin E Recommendations for Older Adults Be Increased?."
- The significance of Vitamin E for Immune: The Role of Vitamin E in Immunity. (Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that can protect the polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the membrane from oxidation, regulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and modulate signal transduction...)
- The impact of Vitamin E on Immune: Role of Vitamin E in Immune System. (Vitamin E is a potent antioxidant and has an ability to modulate host immune functions...)
- The significance of Vitamin E for Immune: The Effects of Oral Supplements With Sambucus Nigra, Zinc, Tyndallized Lactobacillus Acidophilus (HA122), Arabinogalactans, Vitamin D, Vitamin E and Vitamin C in Otitis Media With Effusion in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. (Objective: To evaluate the ability of oral supplements with immune-stimulating molecules (Sambucus nigra, Zinc, Tyndallized Lactobacillus acidophilus (HA122), Arabinogalactans, vitamin D, vitamin E and vitamin C) to reduce the inflammation of the upper airway tract and improve the outcome of otitis media with effusion (OME) in children... OS with immune-stimulating molecules should be considered as a supporting therapy in children affected by recurrent episodes of UAI associated with OME due to their capacity to improve the immune response and reduce the inflammatory phenomena. OS can improve the fibroendoscopic findings by restoring middle ear ventilation, in addition to their ability to reduce inflammation in the middle ear.)
- The role of Vitamin E in Immune: Role of Vitamins D, E and C in Immunity and Inflammation. (Inflammatory responses are operationally characterized by pain, redness, heat and swelling at the site of infection and trauma... OS with immune-stimulating molecules should be considered as a supporting therapy in children affected by recurrent episodes of UAI associated with OME due to their capacity to improve the immune response and reduce the inflammatory phenomena. OS can improve the fibroendoscopic findings by restoring middle ear ventilation, in addition to their ability to reduce inflammation in the middle ear.)
Previous article
The Role of Vitamin E in Immunity.

























































