Johra Fatima Tuj, et al.
Antioxidants, 2020
Abstract
Carotenoids are natural lipid-soluble antioxidants abundantly found as colorful pigments in fruits and vegetables. At least 600 carotenoids occur naturally, although about 20 of them, including β-carotene, α-carotene, lycopene, lutein, zeaxanthin, meso-zeaxanthin, and cryptoxanthin, are detectable in the human blood. They have distinct physiological and pathophysiological functions ranging from fetal development to adult homeostasis. β-carotene is a precursor of vitamin A that essentially functions in many biological processes including vision. The human macula lutea and eye lens are rich in lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin, collectively known as macular xanthophylls, which help maintain eye health and prevent ophthalmic diseases. Ocular carotenoids absorb light from the visible region (400-500 nm wavelength), enabling them to protect the retina and lens from potential photochemical damage induced by light exposure. These natural antioxidants also aid in quenching free radicals produced by complex physiological reactions and, consequently, protect the eye from oxidative stress, apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation. This review discusses the protective mechanisms of macular xanthophylls in preventing eye diseases such as cataract, age-related macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy. Moreover, some preclinical animal studies and some clinical trials are discussed briefly to understand carotenoid safety and efficacy.
Keywords
age-related macular degeneration; carotenoids; cataract; diabetic retinopathy; eye disease; lutein; oxidative stress; xanthophylls; zeaxanthin; β-carotene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.Figures
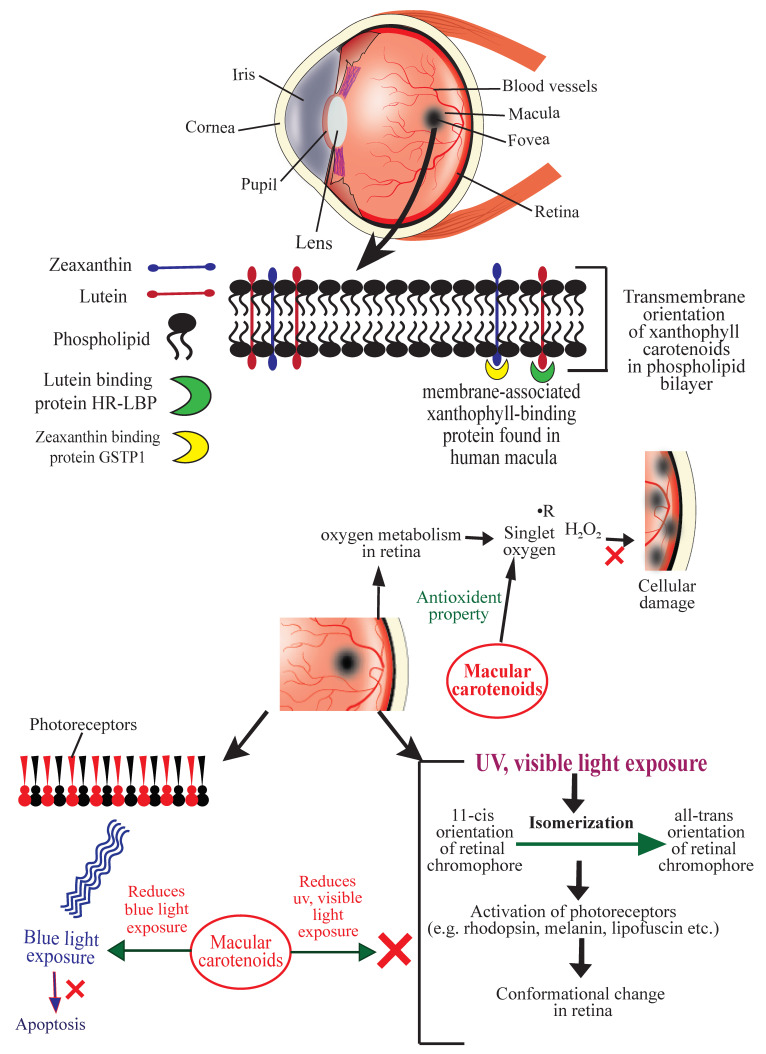
Schematic diagram showing the mechanisms of action of carotenoids to prevent age-related macular degeneration (AMD). HR-LBP: human retinal lutein-binding protein; GSTP1: glutathione S-transferase Pi 1; R: free radical (symbolic representation).
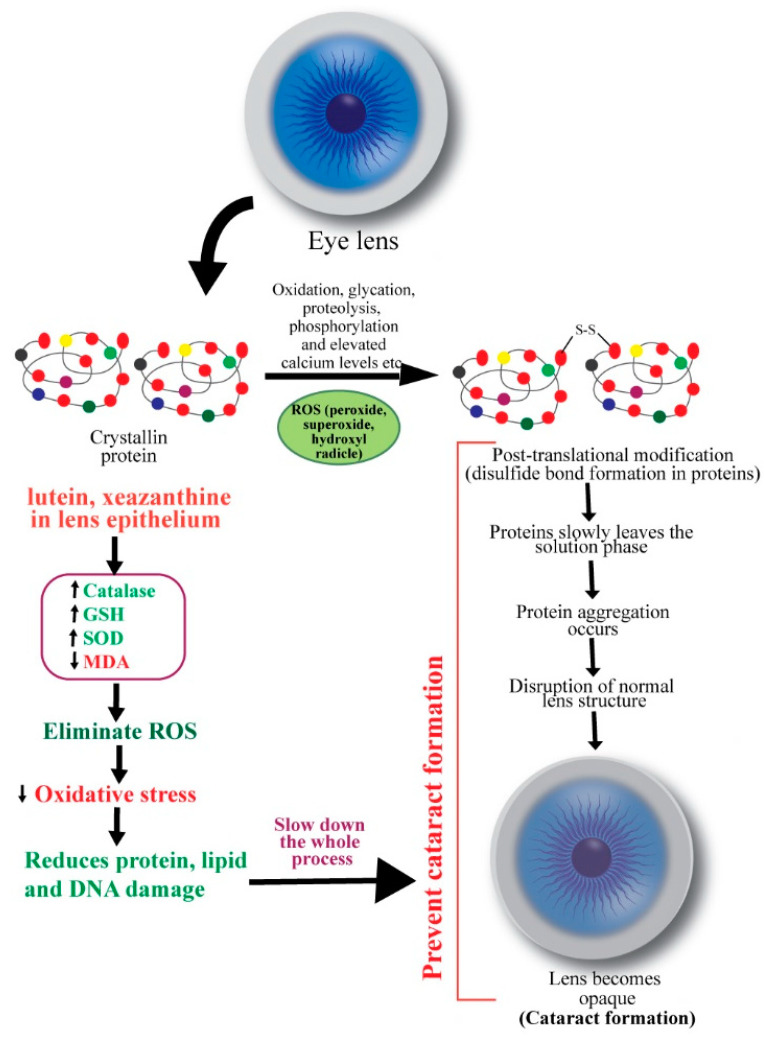
Schematic diagram showing the mechanisms of action of carotenoids to prevent cataract. ROS: reactive oxygen species.
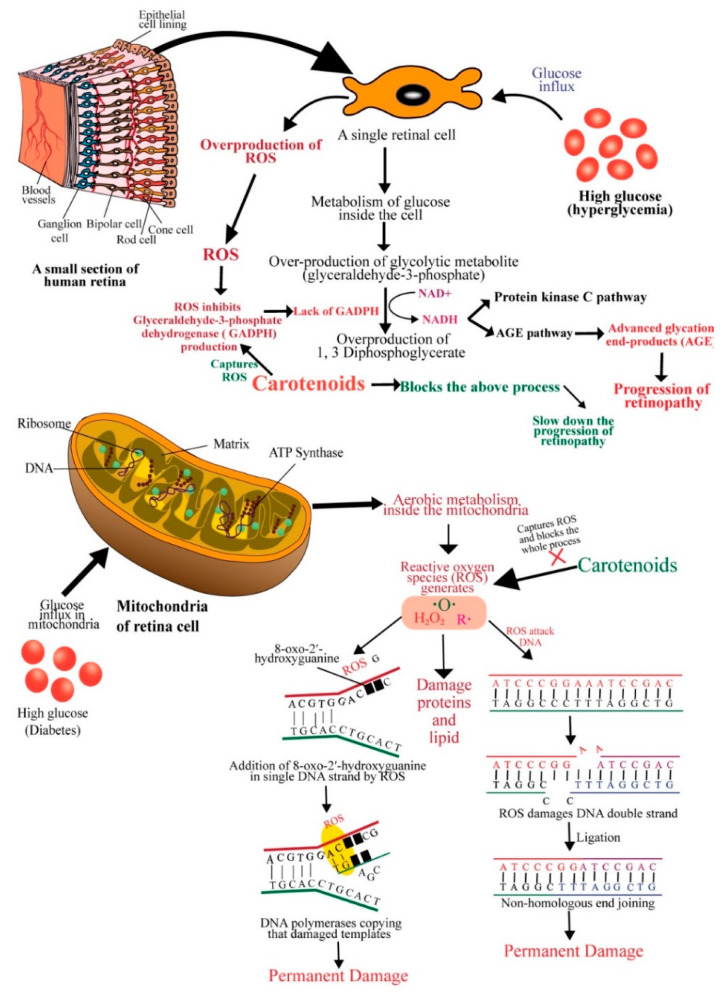
Schematic diagram showing the mechanisms of action of carotenoids to prevent diabetic retinopathy. ROS: reactive oxygen species; GADPH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; AGE: advanced glycation end-product; DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid; ATP: adenosine triphosphate.
| PMID: | 33114699 |
|---|---|
| PMCID (Free PMC Article): | PMC7692753 |
| DOI: | 10.3390/antiox9111046 |
| Category: | Eye Health |
The best supplements with Lycopene, Canthaxanthin, Zeaxanthin or Lutein in Eye Health category:
- 1MD - VisionMD™ -
VisionMD™ - Complete Vision & Eye Support
VisionMD™ exceeds the National Eye Institute’s extensive eye health nutrient recommendations, based on the comprehensive AREDS 2 & CARMIS clinical studies. It contains among others: Lycopene, Zeaxanthin, Lutein. - Healthy Vision, 60 Vegan Liquid Phyto-Caps (Gaia Herbs) - Purity - Keep it CleanAll products are screened for pesticides, microbes & heavy metals. It contains among others: Lutein.
- Lutein, 10 mg, 120 Softgels (Now Foods) - Lutein is an orange-red carotenoid pigment produced by plants and is present in the diet in colorful fruits and vegetables. It contains among others: Lutein.
- Lutein, Double Strength, 90 Veg Capsules (Now Foods) - Lutein is an orange-red carotenoid pigment produced by plants and is present in the diet in color fruits and vegetables. It contains among others: Zeaxanthin, Lutein.
- Astaxanthin, 10 mg, 60 Softgels (Now Foods) - NOW Astaxanthin is a naturally occurring carotenoid that, due to its unique structure, performs an important role in cellular free radical protection and healthy immune system responses. It contains among others: Canthaxanthin, Lutein.
- Lutein & Zeaxanthin, 60 Softgels (Now Foods) - Lutein and Zeaxanthin are free radical scavenging carotenoid pigments often found together in vegetables. It contains among others: Zeaxanthin, Lutein.
Articles similar to "A Mechanistic Review of β-Carotene, Lutein, and Zeaxanthin in Eye Health and Disease."
- The impact of Lutein on Eye Health: Lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin: The basic and clinical science underlying carotenoid-based nutritional interventions against ocular disease. (The human macula uniquely concentrates three carotenoids: lutein, zeaxanthin, and meso-zeaxanthin...)
- The impact of Lutein on Eye Health: Nutritional supplements for age-related macular degeneration. (PURPOSE OF REVIEW: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of visual loss in older adults, has limited therapeutic options...)
- The significance of Lutein for Eye Health: The relationship of dietary carotenoid and vitamin A, E, and C intake with age-related macular degeneration in a case-control study: AREDS Report No. 22. (OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the relationship of dietary carotenoids, vitamin A, alpha-tocopherol, and vitamin C with prevalent age-related macular degeneration (AMD) in the Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS)... Higher dietary intake of lutein/zeaxanthin was independently associated with decreased likelihood of having neovascular AMD, geographic atrophy, and large or extensive intermediate drusen.)
- The role of Lutein in Eye Health: Lutein and zeaxanthin supplementation and association with visual function in age-related macular degeneration. (PURPOSE: To evaluate the effects of lutein and zeaxanthin on visual function in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of AMD patients... Lutein and zeaxanthin supplementation is a safe strategy for improving visual performance of AMD patients, which mainly showed in a dose-response relationship. )
- The significance of Lutein for Eye Health: Role of lutein supplementation in the management of age-related macular degeneration: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. (OBJECTIVE: The conduct of this meta-analysis aimed at examining the individual role of lutein as a dietary supplement in improving conditions of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) from the data generated from randomized controlled trials (RCTs)... A statistically highly significant effect of lutein supplementation has been observed for improving the MPOD, whereas the improvement in VA was milder. A daily dose of 10 mg was found as effective as higher doses in this meta-analysis. However, the number of input studies is not adequate for conclusive evidence. )
- The role of Lutein in Eye Health: Lutein and zeaxanthin intake and the risk of age-related macular degeneration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. (Lutein and zeaxanthin are thought to decrease the incidence of age-related macular degeneration (AMD); however, findings have been inconsistent... A statistically highly significant effect of lutein supplementation has been observed for improving the MPOD, whereas the improvement in VA was milder. A daily dose of 10 mg was found as effective as higher doses in this meta-analysis. However, the number of input studies is not adequate for conclusive evidence. )
Previous article
Ophthalmologic evaluation in vitamin-E deficiency: A case report.

























































