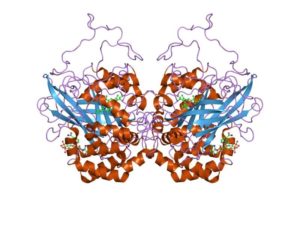
The properties of Catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals). It catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. Low levels of catalase may play a role in the graying process of human hair. Hydrogen peroxide is naturally produced by the body and broken down by catalase. If catalase levels decline, hydrogen peroxide cannot be broken down so well. The hydrogen peroxide interferes with the production of melanin, the pigment that gives hair its color.