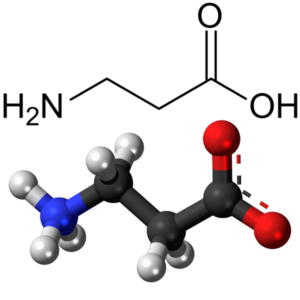
The properties of Beta-Alanine
β-Alanine is not found in any major proteins or enzymes. It is a component of the naturally occurring peptides carnosine and anserine and also of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), which itself is a component of coenzyme A. Under normal conditions, β-alanine is metabolized into acetic acid.
β-Alanine is the rate-limiting precursor of carnosine, which is to say carnosine levels are limited by the amount of available β-alanine, not histidine.[6] Supplementation with β-alanine has been shown to increase the concentration of carnosine in muscles, decrease fatigue in athletes and increase total muscular work done. Simply supplementing with carnosine is not as effective as supplementing with β-alanine alone since carnosine, when taken orally, is broken down during digestion to its components, histidine and β-alanine. Hence, by weight, only about 40% of the dose is available as β-alanine.
Athletic performance enhancement. There is evidence that β-alanine supplementation can increase exercise and cognitive performance.