Jemaa Houda Ben, et al.
African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines, 2017
Abstract
Background
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common endocrinal disorders and medicinal plants continue to play an important role in the management of this disease. In this study, Rosa canina was investigated for the antioxidant and α-amylase inhibition activities.
Materials and Methods
Methanolic extract of Rosa canina was investigated for its potential antioxidant activity. The extracts' total phenolic and flavonoid contents and scavenging capacity for free radicals were evaluated. The α-amylase inhibition assay was also carried.
Results
Rosa canina extract exhibits a total Phenolic and flavonoid levels respectively (21.918 mg GAE/g and 2.647mg ER/g). The free radical scavenging activity was found to be prominent against DPPH with an IC50 of 0.668 mg/ml and against ABTS with an IC50 of 0.467 mg/ml. Extract showed a significant ferric ion reducing activities with an IC50 of4.962 mg/ml.
Conclusion
Rosa canina exerted a higher inhibitory activity against α-amylase. The obtained results support the antidiabetic use of rosa canina.
Keywords
Rosa canina; antioxidant activity; hyperglycemia; phytochemical profile; α-amylase.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.Figures
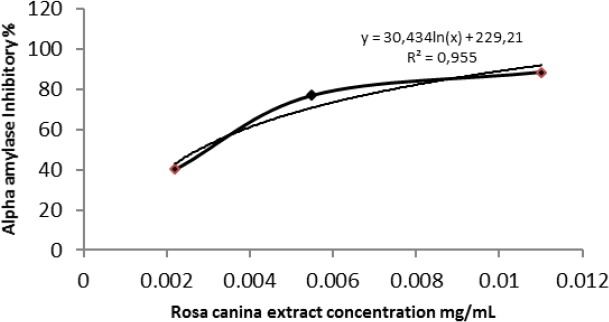
α-amylase inhibitory activity of different concentrations of Rosa canina extract
| PMID: | 28573216 |
|---|---|
| DOI: | 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i2.1 |
| PMCID (Free PMC Article): | PMC5446433 |
| Category: | Diabetes / Blood Sugar |
Previous article
Phytochemistry, Traditional Uses and Pharmacological Profile of Rose Hip: A Review.

























































