Montserrat-de la Paz Sergio, et al.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 2014
Abstract
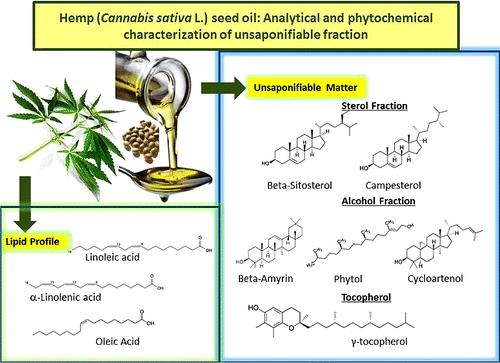
Non-drug varieties of Cannabis sativa L., collectively namely as "hemp", have been an interesting source of food, fiber, and medicine for thousands of years. The ever-increasing demand for vegetables oils has made it essential to characterize additional vegetable oil through innovative uses of its components. The lipid profile showed that linoleic (55%), α-linolenic (16%), and oleic (11%) were the most abundant fatty acids. A yield (1.84-1.92%) of unsaponifiable matter was obtained, and the most interesting compounds were β-sitosterol (1905.00 ± 59.27 mg/kg of oil), campesterol (505.69 ± 32.04 mg/kg of oil), phytol (167.59 ± 1.81 mg/kg of oil), cycloartenol (90.55 ± 3.44 mg/kg of oil), and γ-tocopherol (73.38 ± 2.86 mg/100 g of oil). This study is an interesting contribution for C. sativa L. consideration as a source of bioactive compounds contributing to novel research applications for hemp seed oil in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic food, and other non-food industries.
Keywords
Cannabis sativa; fatty acids; hemp; phytol; sterols; tocopherols; vegetable oils.
| PMID: | 24422510 |
|---|---|
| DOI: | 10.1021/jf404278q |
| Additional information: | Read more about hemp oil: Kannaway ™ Gold Premium Hemp Oil. |
| Category: | General properties of Cannabis Sativa |
| Category: | General properties of Cannabidiol |
| Category: | Hemp Products |
The best supplements with Cannabis Sativa or Cannabidiol in Hemp Products category:
- Provacan CBD Oil Spray 1200mg - Our 1200mg CBD spray is the most popular spray option that we offer here at Provacan. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- Aspen Green - Pure Science Full Spectrum Hemp Oil 3000mg - Our 1 oz (30mL) 3000 mg Full Spectrum Hemp Oil is made from our Colorado USDA Certified Organic Full Spectrum Hemp Extract. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- EMPE - CBD Full Spectrum Hemp Oil Tincture - Hemp oils are naturally prepared with a smooth texture and organic taste. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- Absolute Nature - Full Spectrum 1000 mg CBG & CBD Oil Drops / Tincture – 30ml - Our top-quality beautifully golden full-spectrum CBG & CBD oil tincture contains not only a high amount of CBG & CBD, but other naturally-occurring cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids, plant proteins, mineral, vitamins, essential fatty acids and other beneficial compounds from the cannabis/hemp plant, providing the best possible benefits without the high. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- Natures Method CBD Oil 300 mg - When used as directed, Natures Method CBD Oil regulates mood patterns and sleep cycle, mitigates inflammatory response, and boosts cognitive performance. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- Swift CBD - sublingual spray - A superior CBD delivery system. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- CBDPure Softgels 750 - CBDPure Softgels 750 has been developed for those wanting a mega-dose of CBD in a single serving and the convenience of a softgel. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- CBDPure Hemp Oil 1000 - CBDPure Hemp Oil 1000 has been developed for those looking for a ultra-high dose of CBD in a tincture. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- Alert – THC-Free CBD Energy Capsules - 30 capsules/300 mg total CBD (Plants Not Pills) - These Focus formula capsules are used by clients to increase alertness and attention. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- Spark Herbal Aphrodisiac CBD Capsules - 20 capsules/400 mg total CBD (Plants Not Pills) - Herbal aphrodisiac capsules with 20mg of organically-grown, THC-free CBD extract in each capsule. It contains among others: Cannabidiol.
- GreenLeaf - CBD Oil - CBD oils have been used and praised by people struggling with various ailments for years. It contains among others: Cannabis Sativa, Cannabidiol.
Articles similar to "Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed oil: analytical and phytochemical characterization of the unsaponifiable fraction."
- The properties of Cannabis Sativa: Cannabis, cannabinoids, and health. (Cannabis (also known as marijuana) is the most frequently used illicit psychoactive substance in the world...)
- The properties of Cannabis Sativa: Analysis of cannabinoids in commercial hemp seed oil and decarboxylation kinetics studies of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA). (Hemp seed oil from Cannabis sativa L...)
- The properties of Cannabis Sativa: Cannabis sativa: Much more beyond Δ 9-tetrahydrocannabinol. (Cannabis is the most used illicit drug worldwide and its medicinal use is under discussion, being regulated in several countries...)
- The properties of Cannabis Sativa: Cannabidivarin-rich cannabis extracts are anticonvulsant in mouse and rat via a CB1 receptor-independent mechanism. (Background and purpose: Epilepsy is the most prevalent neurological disease and is characterized by recurrent seizures...)
- The properties of Cannabis Sativa: Molecular Pharmacology of Phytocannabinoids. (Cannabis sativa has been used for recreational, therapeutic and other uses for thousands of years...)
- The properties of Cannabis Sativa: Pharmacology of cannabinoids in the treatment of epilepsy. (The use of cannabis products in the treatment of epilepsy has long been of interest to researchers and clinicians alike; however, until recently very little published data were available to support its use...)
- The properties of Cannabis Sativa: Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of the plant cannabinoids, delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and cannabinol. (Increasing interest in the biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of cannabinoids and in the development of cannabinoid medications necessitates an understanding of cannabinoid pharmacokinetics and disposition into biological fluids and tissues...)
- The impact of Cannabidiol on Hemp Products: Medical use of cannabinoids. (Cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoids and the enzymes responsible for their biosynthesis and degradation constitute the endocannabinoid system...)
- The significance of Cannabidiol for Hemp Products: Use of cannabidiol (CBD) for the treatment of chronic pain. (Chronic pain can be recurrent or constant pain that lasts for longer than 3 months and can result in disability, suffering, and a physical disturbance...)
- The role of Cannabidiol in Hemp Products: Effectiveness of cannabidiol oil for pediatric anxiety and insomnia as part of posttraumatic stress disorder: a case report. (INTRODUCTION:Anxiety and sleep disorders are often the result of posttraumatic stress disorder and can contribute to an impaired ability to focus and to demonstration of oppositional behaviors...)
- The significance of Cannabidiol for Hemp Products: The composition of hemp seed oil and its potential as an important source of nutrition. (The fatty acid and natural product content of hemp seed oil was analyzed by GC-MS and LC-MS...)
- The role of Cannabidiol in Hemp Products: Cannabis-based medicines for chronic neuropathic pain in adults. ( This review is one of a series on drugs used to treat chronic neuropathic pain... The potential benefits of cannabis-based medicine (herbal cannabis, plant-derived or synthetic THC, THC/CBD oromucosal spray) in chronic neuropathic pain might be outweighed by their potential harms. The quality of evidence for pain relief outcomes reflects the exclusion of participants with a history of substance abuse and other significant comorbidities from the studies, together with their small sample sizes. )
- The impact of Cannabidiol on Hemp Products: The Role of Cannabidiol (CBD) in Chronic Pain Management: An Assessment of Current Evidence. (Purpose of review: Given the growing challenges in chronic pain management coupled with the ongoing consequences of the opioid epidemic, pain management practitioners are looking into more effective, innovative, and safer alternatives to treat pain... The potential benefits of cannabis-based medicine (herbal cannabis, plant-derived or synthetic THC, THC/CBD oromucosal spray) in chronic neuropathic pain might be outweighed by their potential harms. The quality of evidence for pain relief outcomes reflects the exclusion of participants with a history of substance abuse and other significant comorbidities from the studies, together with their small sample sizes. )
- The significance of Cannabidiol for Hemp Products: Cannabidiol, cannabinol and their combinations act as peripheral analgesics in a rat model of myofascial pain. (Objective: This study investigated whether local intramuscular injection of non-psychoactive cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD), cannabinol (CBN), cannabichromene (CBC) and their combinations can decrease nerve growth factor (NGF)-induced masticatory muscle sensitization in female rats... These results suggest that peripheral application of these non-psychoactive cannabinoids may provide analgesic relief for chronic muscle pain disorders such as temporomandibular disorders and fibromyalgia without central side effects. )
Previous article
The cannabinoid system and immune modulation.
Next article
The composition of hemp seed oil and its potential as an important source of nutrition.

























































